Authentication With WebAuthn & Passkeys

This feature is available to licensed FusionAuth instances as of version 1.52.0. A free license is available in the Plan tab for any user who registers in the account portal.
Available since 1.41.0
Overview#
WebAuthn is a W3C specification that defines an API to create and use public-key credentials in web applications that provides the ability for users to authenticate in their browser using the same method they use to unlock their device, like a biometric scan or PIN. WebAuthn has some big security benefits over the traditional username and password. Continue reading to learn how you can integrate WebAuthn with your FusionAuth instance. If you’re an administrator looking for details on configuring WebAuthn in your FusionAuth instance, check out the WebAuthn Admin Guide. If you want more information on the basics of WebAuthn and its security benefits, FusionAuth’s WebAuthn blog post is a good place to start.
What about passkeys?
“Passkey” is the user-friendly term for WebAuthn credentials. Use this guide to integrate FusionAuth’s WebAuthn systems with your application login to allow your users to log in with passkeys.
Video Walkthrough For Community License#
If you’re already using the Community plan, you’ll need to upgrade to 1.52.0 to get passkeys. Regardless of whether you’re a new or existing user, you’ll need to register for a free license of FusionAuth. Our Admin UI will walk you through the process. Your free license is good forever, and will remain active as we add even more features to the Community plan over time.
Setting Up For WebAuthn#
If you are planning to use WebAuthn, you have two options. The first option is the FusionAuth hosted login pages interface. FusionAuth’s hosted login pages are customizable via themes to make each of the web pages look like your application. The other option is using the WebAuthn API. Both approaches are covered in the sections below.
In either case, you should:
- Enable WebAuthn under the “WebAuthn” tab of the tenant configuration:
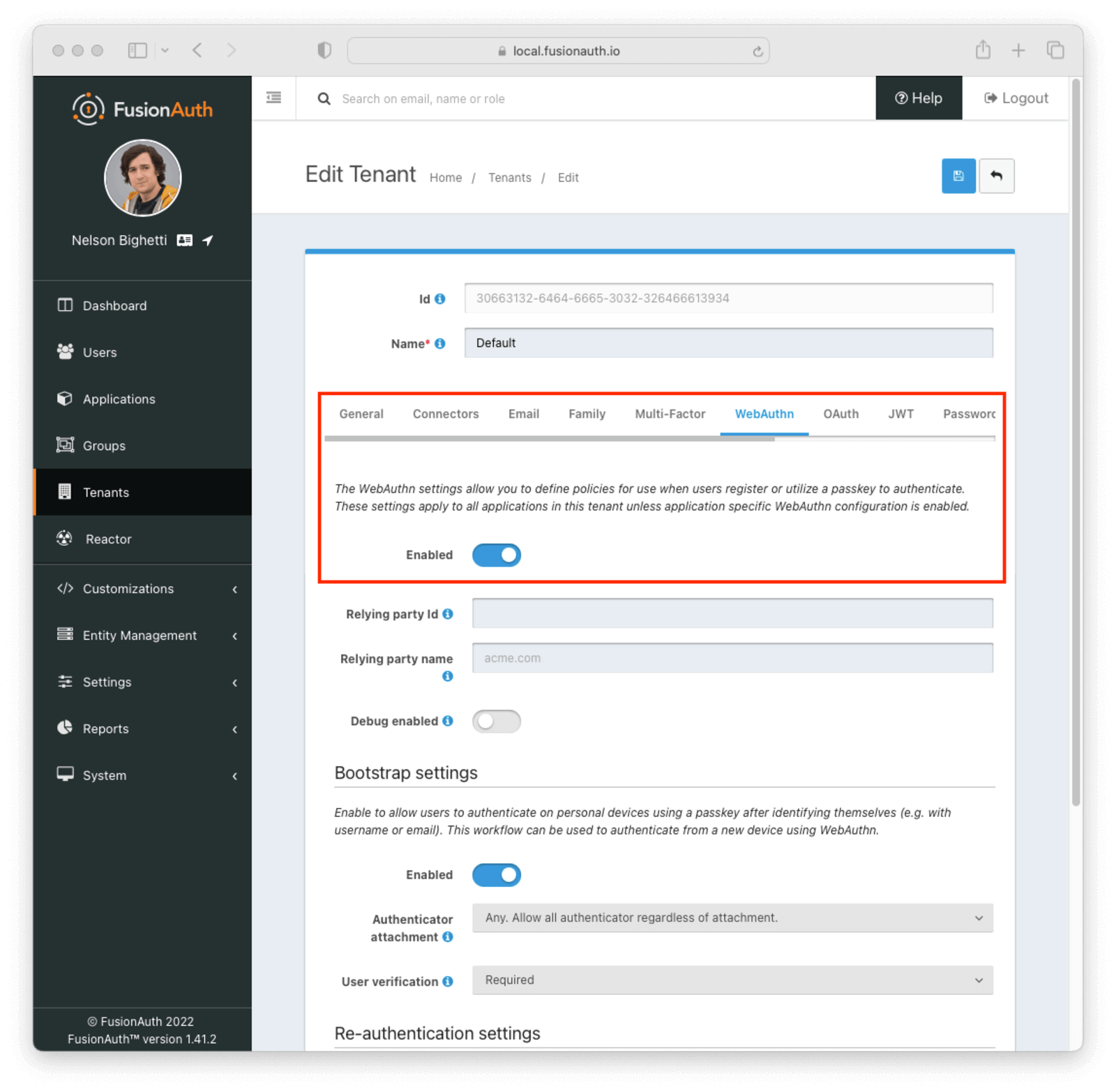
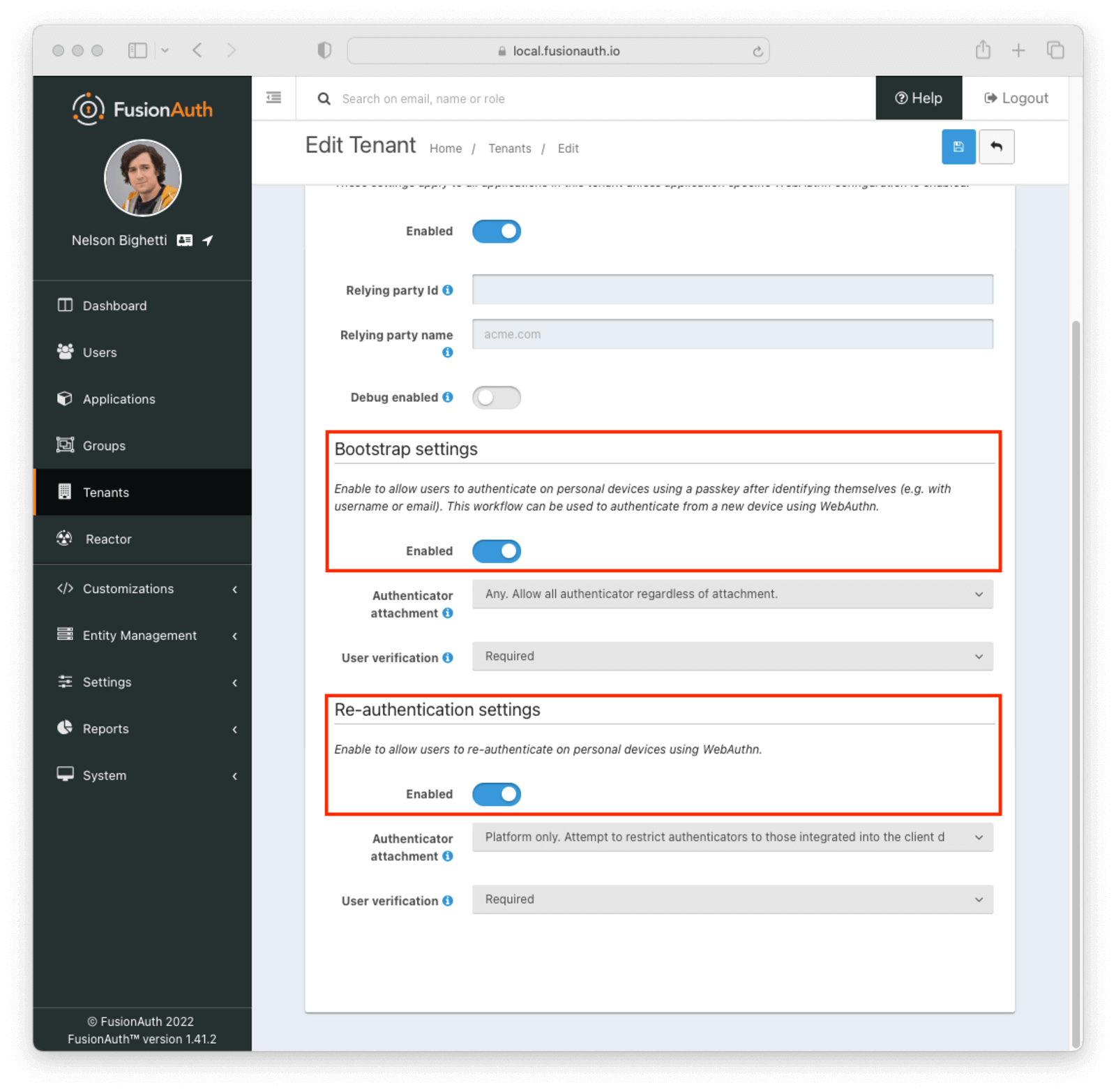
- Enable one or more WebAuthn workflows on the tenant configuration:
- Add a user and register them with an application belonging to the tenant
The WebAuthn Admin Guide has more information on the tenant configuration options and overriding workflow availability per application.
Using the FusionAuth Hosted Login Pages#
Using the FusionAuth hosted login pages will handle the client-side portion of WebAuthn ceremonies for you. This includes necessary data conversions between the FusionAuth APIs and the WebAuthn JavaScript API as well as the WebAuthn API call itself. There is no additional configuration required for this approach.
FusionAuth supports two WebAuthn workflows: re-authentication and bootstrap authentication.
Re-authentication#
The re-authentication workflow is used to provide a streamlined user experience for repeated logins from the same device. FusionAuth will automatically prompt users to opt in to this workflow when it detects a compatible device. The next time the user is prompted to sign in, they will be redirected to a WebAuthn re-authentication page that lists available passkeys. The user can sign in by clicking a passkey in the list and completing the WebAuthn authentication ceremony.
Registration#
After a successful login, users will automatically be redirected to prompt them to register or select a WebAuthn passkey for re-authentication if:
- The re-authentication workflow is enabled
- FusionAuth detects a device suitable for re-authentication using the isUserVerifyingPlatformAuthenticatorAvailable() JavaScript method
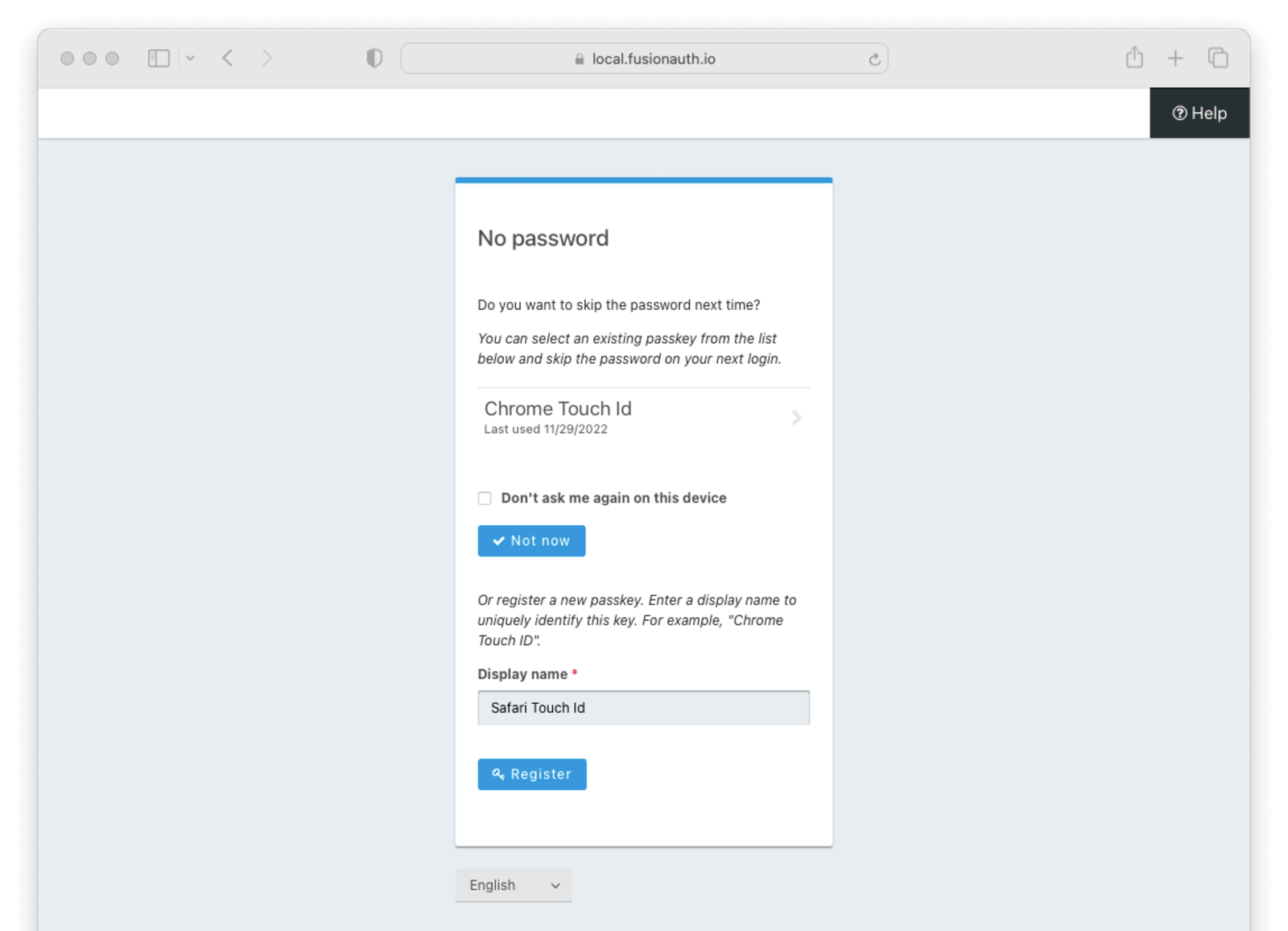
The re-authentication prompt page lists a user’s WebAuthn passkeys that meet the attachment and user verification requirements for the tenant configuration. It also has a section to register a new passkey for re-authentication.
There are a few important notes about this page:
- The listed passkeys may have been registered with an authenticator that is not currently available (e.g. a removable security key)
- The listed passkeys may have been registered in another browser. Typically passkeys registered with a platform authenticator in one browser will not work in a different browser
- If the user tries to register a new passkey using the same authenticator as another of their passkeys, the registration ceremony will fail
The user is also presented with the option to skip selecting a re-authentication passkey. Choosing the “Don’t ask me again on this device” and then clicking the Not now button will skip the prompt to sign in with a passkey in the future.
The user can select a passkey from the list to complete a WebAuthn authentication ceremony and mark that passkey for re-authentication. Otherwise, they can enter a display name and complete a WebAuthn registration ceremony to generate a new passkey that will be marked for re-authentication. In either case, FusionAuth will redirect to the WebAuthn re-authentication page the next time a login page would be presented.
Authentication#
When a user visits the hosted login pages and begins an authentication, FusionAuth will check to see if the user has previously set up a passkey for this device. If this can be determined, the user will be redirected to the WebAuthn re-authentication page.
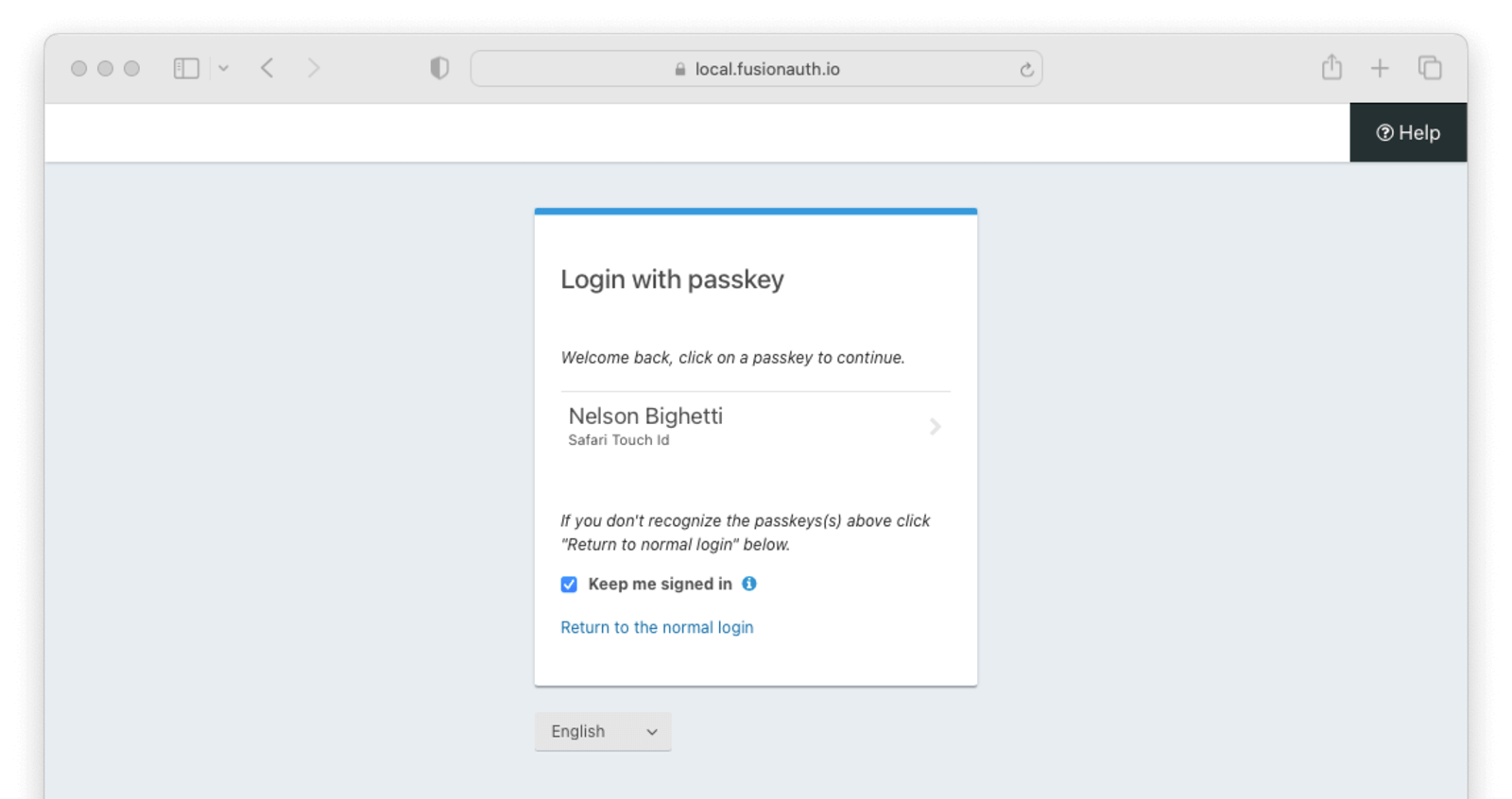
WebAuthn passkeys determined to be present will be listed. A user can select which passkey and, by extension, account they would like to use for re-authentication. Clicking a passkey on the list will start the WebAuthn authentication ceremony. Only the selected passkey will be eligible to complete the re-authentication. Once the WebAuthn authentication ceremony has been completed successfully, the user will be authenticated.
The user also has the option to return to the normal login page by clicking the Return to the normal login link.
These pages can be modified by the themes just as any other hosted login page.
Bootstrap Authentication#
The bootstrap workflow requires that the user “bootstrap” the WebAuthn authentication ceremony by providing identifying information such as a username or email address. You could think of this as a “manual” WebAuthn login as opposed to the re-authentication workflow where users are automatically prompted. Users can use any of their passkeys whose authenticator meets the attachment and user verification requirements to complete this authentication process.
Registration#
If the re-authentication workflow is disabled for the tenant, users need another way to register passkeys for WebAuthn bootstrap authentication because they won’t be prompted to add a passkey during authentication. Users can register and manage their own passkeys through Self Service Account Management.
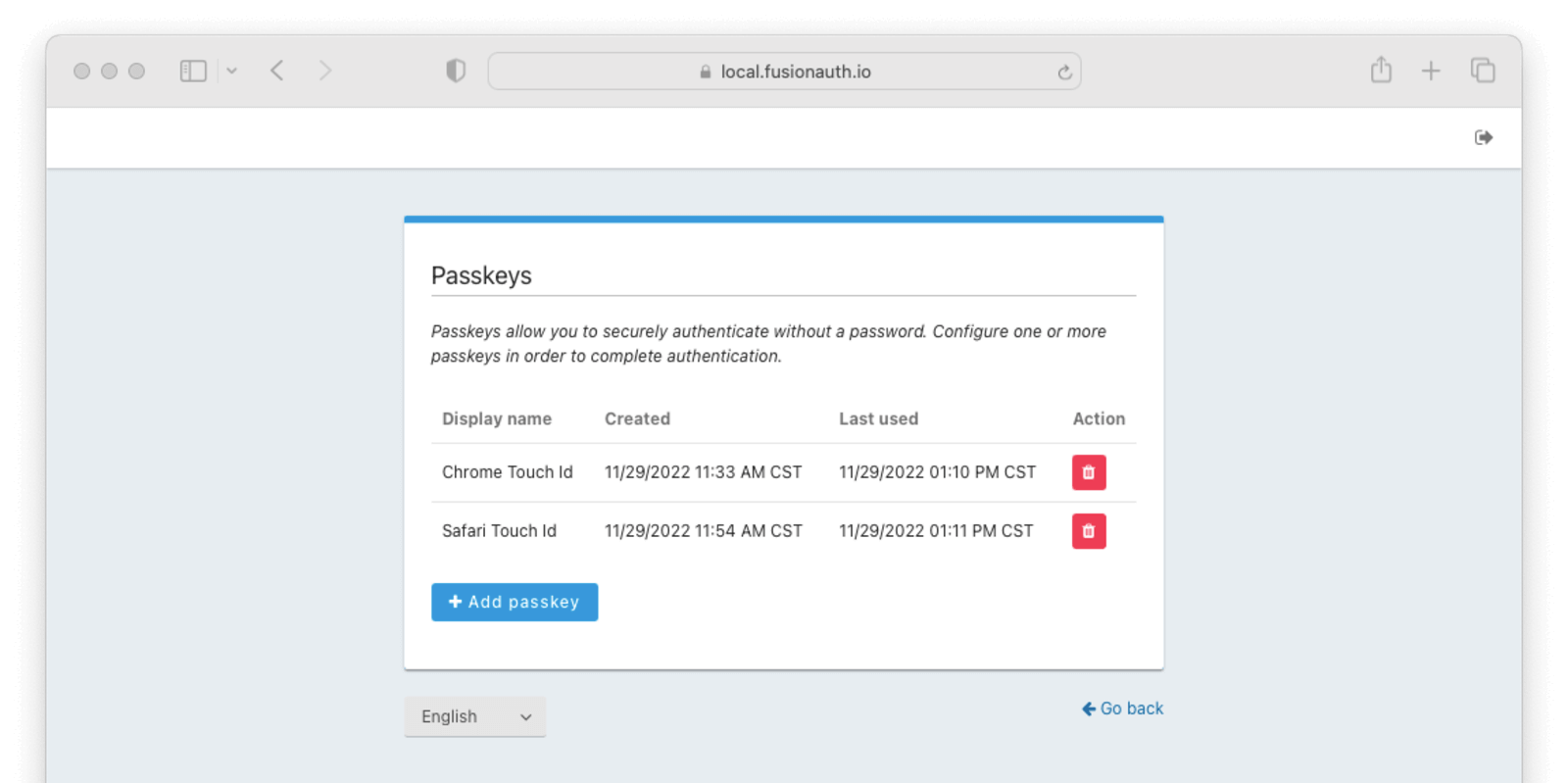
Users can see a list of passkeys along with a button to delete each one. Below the list of registered passkeys is a button to add a new passkey. Passkey registration on this page will use authenticator attachment and user verification requirements designed to cover the broadest set of use cases. Depending on the tenant configuration, passkeys registered here may not be usable with all enabled WebAuthn workflows. For instance, if passkey ABC is cross-platform, but the tenant is only configured to accept platform authenticators, passkey ABC won’t work even though it shows up in this list.
Authentication#
If the bootstrap workflow is enabled, users will see a button to authenticate with “Fingerprint, device or key” on the initial FusionAuth login page.
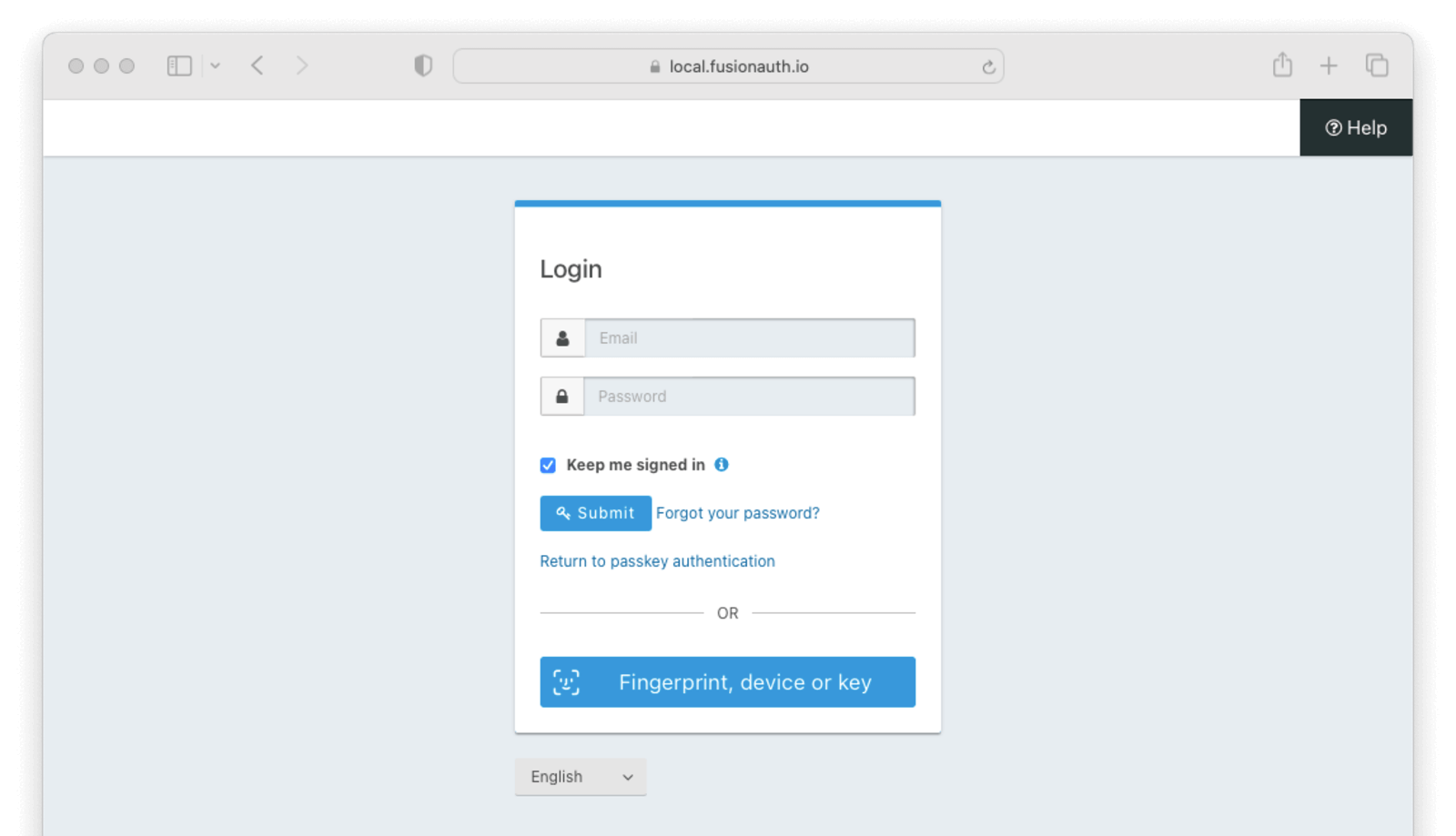
When a re-authentication passkey has been registered in this browser, users will see a link just above the alternative login methods sections with the text “Return to passkey authentication.” This link will take the user back to the re-authentication page.
Clicking the Fingerprint, device or key button will take the user to the WebAuthn bootstrap login page.
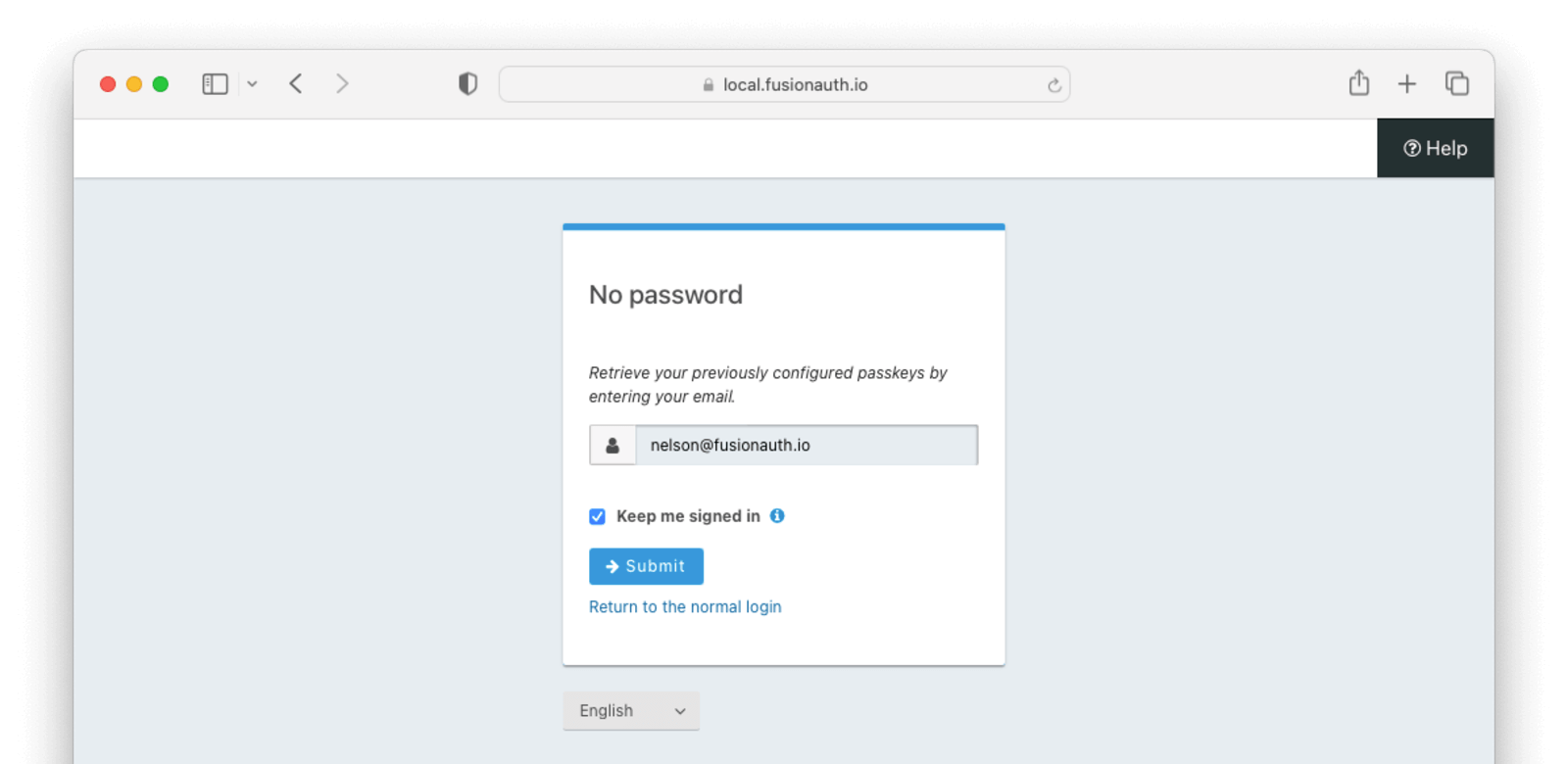
The user must identify themselves with their username, email address, or phone number, then click the Submit button to begin the WebAuthn authentication ceremony. They can use any of their registered passkeys whose authenticator meets the configured attachment and user verification requirements for the bootstrap workflow.
Once the WebAuthn authentication ceremony has been completed successfully, the user will be authenticated.
These pages can be modified by the themes just as any other hosted login page.
Using the API Directly#
While using the FusionAuth’s hosted login pages works for many, you may need more control. You can use the WebAuthn API to register new passkeys and authenticate a user with a passkey. The WebAuthn API reference docs cover each of the API calls, but this guide will walk you through an implementation.
There are a couple of reasons you might choose this method of integration.
- You can customize every part of the user login experience
- You can use a different method to track re-authentication passkey availability
When using this option, you must set up an API key with the appropriate permissions. The minimum level of privilege required is the POST permission to the /api/webauthn/start and /api/webauthn/register/start endpoints.
The WebAuthn registration and authentication ceremonies both have a similar set of steps.
- Start the WebAuthn ceremony via an API call to FusionAuth
- Transform the API response containing the options for the ceremony
- Invoke the WebAuthn JavaScript API in the browser using the transformed options
- Transform the authenticator response to prevent issues during network transport
- Include the transformed response in an API call to FusionAuth to complete the ceremony
The registration and authentication ceremonies are covered in their own sections below.
Registration#
Use the WebAuthn registration ceremony to create a new passkey for a user.
Starting the Registration#
You start a WebAuthn registration by calling the /api/webauthn/register/start endpoint.
API_KEY=...
REQUEST_PAYLOAD='{...}'
curl -H "Content-type: application/json" -H "Authorization: $API_KEY" https://local.fusionauth.io/api/webauthn/register/start -d $REQUEST_PAYLOADStart WebAuthn Registration API call
Here’s an example request payload:
Start WebAuthn Registration Request JSON
{
"displayName": "Chrome Touch ID",
"userId": "703fe2d2-2d39-4cb7-b76d-0b9918ed2457",
"workflow": "reauthentication"
}The call to /api/webauthn/register/start begins the registration ceremony and returns a response with options for the WebAuthn JavaScript API, including a one-time challenge specific to this ceremony:
Start WebAuthn Registration Response JSON
{
"options": {
"attestation": "none",
"authenticatorSelection": {
"authenticatorAttachment": "platform",
"userVerification": "required"
},
"challenge": "fdnW2u1_Nk9_FY2SprU4mPs0NgBTbo9tOO5Q9EvO1Oc",
"excludeCredentials": [
{
"id": "MBU0eBsaNAt4VEh4Lbn2sQ==",
"transports": [
"internal"
],
"type": "public-key"
}
],
"extensions": {
"credProps": true
},
"pubKeyCredParams": [
{
"alg": -36,
"type": "public-key"
},
{
"alg": -35,
"type": "public-key"
},
{
"alg": -7,
"type": "public-key"
},
{
"alg": -39,
"type": "public-key"
},
{
"alg": -38,
"type": "public-key"
},
{
"alg": -37,
"type": "public-key"
},
{
"alg": -259,
"type": "public-key"
},
{
"alg": -258,
"type": "public-key"
},
{
"alg": -257,
"type": "public-key"
}
],
"rp": {
"id": "piedpiper.com",
"name": "Pied Piper"
},
"timeout": 180000,
"user": {
"displayName": "Chrome Touch ID",
"id": "NzAzZmUyZDItMmQzOS00Y2I3LWI3NmQtMGI5OTE4ZWQyNDU3",
"name": "richard@fusionauth.io"
}
}
}Transform the Options Response#
Certain fields on the /api/webauthn/register/start response are returned as base64url-encoded strings. These have to be translated to JavaScript ArrayBufferss before being passed to the WebAuthn JavaScript API. The response should be left as-is other than the transformations for these particular fields.
The following response fields need to be converted to ArrayBuffers if they are present:
- options.challenge
- options.excludeCredentials[x].id
- options.user.id
See the /api/webauthn/register/start response body section for more details.
You can use the following JavaScript function to perform the conversion:
Function to convert a base64url-encoded string to an ArrayBuffer
function base64URLToBuffer(base64URL) {
const base64 = base64URL.replace(/-/g, '+').replace(/_/g, '/');
const padLen = (4 - (base64.length % 4)) % 4;
return Uint8Array.from(atob(base64.padEnd(base64.length + padLen, '=')), c => c.charCodeAt(0));
}The following is an ES6 JavaScript snippet to convert the API response to the object that is passed to the WebAuthn JavaScript API. In the following example options is the value of the options field on the /api/webauthn/register/start API response, and creationOptions is the object that is passed to the WebAuthn JavaScript API’s navigator.credentials.create() function.
const creationOptions = {
// publicKey indicates this is for WebAuthn
publicKey: {
...options,
challenge: base64URLToBuffer(options.challenge),
excludeCredentials: options.excludeCredentials?.map(c => {
return {
...c,
id: base64URLToBuffer(c.id)
}
}) ?? [],
user: {
...options.user,
id: base64URLToBuffer(options.user.id)
}
}
};Transform API response for WebAuthn JavaScript API
Invoke the WebAuthn JavaScript API#
Invoke navigator.credentials.create() on the WebAuthn JavaScript API, passing the transformed FusionAuth API response (creationOptions in the snippet above) as a parameter.
The function returns a Promise that resolves with a PublicKeyCredential. Reference MDN documentation or the WebAuthn specification for details.
Transform the Authenticator Response#
Certain fields on the PublicKeyCredential response from the navigator.credentials.create() WebAuthn JavaScript API call need to be transformed from ArrayBuffers to base64url-encoded strings for transport over the network.
The following response fields need to be converted from ArrayBuffers to base64url-encoded strings if they are present where credential refers to the PublicKeyCredential returned by the navigator.credentials.create() call:
- credential.response.attestationObject
- credential.response.clientDataJSON
See the /api/webauthn/register/complete request body section for more details.
You can use the following JavaScript function to perform the conversion:
Function to convert an ArrayBuffer to a base64url-encoded string
function bufferToBase64URL(buffer) {
const bytes = new Uint8Array(buffer);
let string = '';
bytes.forEach(b => string += String.fromCharCode(b));
const base64 = btoa(string);
return base64.replace(/\+/g, '-').replace(/\//g, '_').replace(/=/g, '');
}You should also use convenience methods on the PublicKeyCredential and its response field to extract information on transports supported by the authenticator and any requested client extension results. The response field contains an AuthenticatorAttestationResponse object after a successful call to navigator.credentials.create(). The following is an ES6 JavaScript snippet to convert the PublicKeyCredential to a suitable format for the FusionAuth /api/webauthn/register/complete API call. In the following example, credential is the PublicKeyCredential object returned by the WebAuthn JavaScript API’s navigator.credentials.create() function, and transformedCredential is the object that will be included in the credential on the FusionAuth /api/webauthn/register/complete API request.
const transformedCredential = {
id: credential.id,
response: {
attestationObject: bufferToBase64URL(credential.response.attestationObject),
clientDataJSON: bufferToBase64URL(credential.response.clientDataJSON)
},
type: credential.type,
clientExtensionResults: credential.getClientExtensionResults(),
transports: typeof credential.response.getTransports === 'undefined' ? [] : credential.response.getTransports()
};Transform WebAuthn JavaScript API response for FusionAuth API request
Completing the Registration#
You complete a WebAuthn registration by calling the /api/webauthn/register/complete endpoint.
REQUEST_PAYLOAD='{...}'
curl -H "Content-type: application/json" https://local.fusionauth.io/api/webauthn/register/complete -d $REQUEST_PAYLOADComplete WebAuthn Registration API call
Here’s an example request payload where credential is the transformedCredential from the snippet above:
Complete WebAuthn Registration Request JSON
{
"credential": {
"clientExtensionResults": {
"credProps": {
"rk": true
}
},
"id": "HdN9wqP9mqOonacmiM2gIjASFYg",
"response": {
"attestationObject": "v2dhdHRTdG109mhhdXRoRGF0YViemPsv4VW-wth0V9gzsxWRFn-1SyC9gM4-QC4ptMFDNhVFAAAAFmhGAxjmXUwbl-q5EoJkWH0AELmJieDlA5kNXEtcIgWnp1a_YTMmYTECYi0xAWItMlggTmZZ1aeY0PP8-Ebdufqcg9TWEs_mJaFJmJ57uRyQ1BxiLTNYIQCzqsN1dkCeZKpWGKEVP0-eqBlkKGNCjfcdg5221SRZX_9jZm10ZG5vbmX_",
"clientDataJSON": "eyJjaGFsbGVuZ2UiOiJ2dHk0WG1ES01EMmxTc2dVOEpsOFlIVEtBcGZlWXpMdkRVUksxTXpGd1JvIiwiY3Jvc3NPcmlnaW4iOmZhbHNlLCJvcmlnaW4iOiJodHRwczovL2Z1c2lvbmF1dGguaW8iLCJ0eXBlIjoid2ViYXV0aG4uY3JlYXRlIn0="
},
"transports": [
"internal"
],
"type": "public-key"
},
"origin": "https://auth.piedpiper.com",
"rpId": "piedpiper.com",
"userId": "703fe2d2-2d39-4cb7-b76d-0b9918ed2457"
}The call to /api/webauthn/register/complete completes the registration ceremony by validating the request against the WebAuthn specification, extracting the public key, and associating the new passkey with the user. This API returns the new WebAuthn passkey registered for the user.
Complete WebAuthn Registration Response JSON
{
"credential": {
"algorithm": -7,
"attestationType": "none",
"authenticatorSupportsUserVerification": true,
"credentialId": "HdN9wqP9mqOonacmiM2gIjASFYg",
"data": {},
"displayName": "Chrome Touch ID",
"name": "richard@fusionauth.io",
"id": "c664318a-2384-4c35-9475-9a200e1d3b72",
"insertInstant": 1668011701792,
"discoverable": false,
"lastUseInstant": 1668021630599,
"publicKey": "-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\nMFkwEwYHKoZIzj0CAQYIKoZIzj0DAQcDQgAEz9DI9AQfZn1aDJG5sw3Ckl7SoQ7E\nLPElDoJMijphvVigTcNMTc8H9Xptl8B20QHMOXGTzaUxLGNY1c8yhw9VVA==\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----",
"relyingPartyId": "piedpiper.com",
"signCount": 41,
"tenantId": "30663132-6464-6665-3032-326466613934",
"transports": [
"internal"
],
"userId": "703fe2d2-2d39-4cb7-b76d-0b9918ed2457"
}
}Authentication#
Use the WebAuthn authentication ceremony to authenticate a user with a passkey. There is also a separate FusionAuth API to complete the assertion, which will validate the authenticator response without logging the user in.
Starting the Authentication#
You start a WebAuthn authentication ceremony by calling the /api/webauthn/start endpoint.
API_KEY=...
REQUEST_PAYLOAD='{...}'
curl -H "Content-type: application/json" -H "Authorization: $API_KEY" https://local.fusionauth.io/api/webauthn/start -d $REQUEST_PAYLOADStart WebAuthn Authentication API call
Here’s an example request payload:
Start WebAuthn Authentication Request JSON
{
"applicationId": "82b24314-95f6-4393-b3da-72c341185244",
"userId": "703fe2d2-2d39-4cb7-b76d-0b9918ed2457",
"workflow": "reauthentication"
}The call to /api/webauthn/start begins the authentication ceremony and returns a response with options for the WebAuthn JavaScript API, including a one-time challenge specific to this ceremony:
Start WebAuthn Authentication Response JSON
{
"options": {
"allowCredentials": [
{
"id": "HdN9wqP9mqOonacmiM2gIjASFYg",
"transports": [
"internal"
],
"type": "public-key"
}
],
"challenge": "fdnW2u1_Nk9_FY2SprU4mPs0NgBTbo9tOO5Q9EvO1Oc",
"rpId": "piedpiper.com",
"timeout": 180000,
"userVerification": "required"
}
}Transform the Options Response#
Certain fields on the /api/webauthn/start response are returned as base64url-encoded strings. These have to be translated to JavaScript ArrayBuffers before being passed to the WebAuthn JavaScript API. The response should be left as-is other than the transformations for these particular fields.
The following response fields need to be converted to ArrayBuffers if they are present:
- options.challenge
- options.allowCredentials[x].id
See the /api/webauthn/start response body section for more details.
You can use the following JavaScript function to perform the conversion:
function base64URLToBuffer(base64URL) {
const base64 = base64URL.replace(/-/g, '+').replace(/_/g, '/');
const padLen = (4 - (base64.length % 4)) % 4;
return Uint8Array.from(atob(base64.padEnd(base64.length + padLen, '=')), c => c.charCodeAt(0));
}The following is an ES6 JavaScript snippet to convert the API response to the object that is passed to the WebAuthn JavaScript API. In the following example options is the value of the options field on the /api/webauthn/start API response, and requestOptions is the object that is passed to the WebAuthn JavaScript API’s navigator.credentials.get() function.
const requestOptions = {
// publicKey indicates this is for WebAuthn
publicKey: {
...options,
challenge: base64URLToBuffer(options.challenge),
allowCredentials: options.allowCredentials.map(c => {
return {
...c,
id: base64URLToBuffer(c.id)
}
})
}
};Transform API response for WebAuthn JavaScript API
Invoke the WebAuthn JavaScript API#
Invoke navigator.credentials.get() on the WebAuthn JavaScript API, passing the transformed FusionAuth API response (requestOptions in the snippet above) as a parameter.
The function returns a Promise that resolves with a PublicKeyCredential. Reference MDN documentation or the WebAuthn specification for details.
Transform the Authenticator Response#
Certain fields on the PublicKeyCredential response from the navigator.credentials.get() WebAuthn JavaScript API call need to be transformed from ArrayBuffers to base64url-encoded strings for transport over the network.
The following response fields need to be converted from ArrayBuffers to base64url-encoded strings if they are present where credential refers to the PublicKeyCredential returned by the navigator.credentials.get() call:
- credential.response.authenticatorData
- credential.response.clientDataJSON
- credential.response.signature
- credential.response.userHandle
See the /api/webauthn/login or /api/webauthn/assert request body sections for more details.
You can use the following JavaScript function to perform the conversion:
Function to convert an ArrayBuffer to a base64url-encoded string
function bufferToBase64URL(buffer) {
const bytes = new Uint8Array(buffer);
let string = '';
bytes.forEach(b => string += String.fromCharCode(b));
const base64 = btoa(string);
return base64.replace(/\+/g, '-').replace(/\//g, '_').replace(/=/g, '');
}You should also use convenience methods on the PublicKeyCredential to extract information on any requested client extension results. The response field contains an AuthenticatorAssertionResponse object after a successful call to navigator.credentials.get(). The following is an ES6 JavaScript snippet to convert the PublicKeyCredential to a suitable format for the FusionAuth /api/webauthn/login or /api/webauthn/assert API call. In the following example, credential is the PublicKeyCredential object returned by the WebAuthn JavaScript API’s navigator.credentials.get() function, and transformedCredential is the object that will be included in the credential field on the FusionAuth API request.
let userHandle = undefined;
if (credential.response.userHandle) {
userHandle = bufferToBase64URL(credential.response.userHandle);
}
const transformedCredential = {
id: credential.id,
response: {
authenticatorData: bufferToBase64URL(credential.response.authenticatorData),
clientDataJSON: bufferToBase64URL(credential.response.clientDataJSON),
signature: bufferToBase64URL(credential.response.signature),
userHandle
},
type: credential.type,
clientExtensionResults: credential.getClientExtensionResults()
};Transform WebAuthn JavaScript API response for FusionAuth API request
Completing the Authentication#
You complete a WebAuthn authentication by calling the /api/webauthn/login endpoint.
REQUEST_PAYLOAD='{...}'
curl -H "Content-type: application/json" https://local.fusionauth.io/api/webauthn/login -d $REQUEST_PAYLOADComplete WebAuthn Authentication API call
Here’s an example request payload where credential is the transformedCredential from the snippet above:
Complete WebAuthn Authentication Request JSON
{
"credential": {
"id": "HdN9wqP9mqOonacmiM2gIjASFYg",
"response": {
"authenticatorData": "mPsv4VW-wth0V9gzsxWRFn-1SyC9gM4-QC4ptMFDNhUFAAAAKQ==",
"clientDataJSON": "eyJjaGFsbGVuZ2UiOiJTeTYzQldla285blFsYzVOQmVWcE1BWjFtQ0hvdzBXUXVFeDRJU2xuQzR3IiwiY3Jvc3NPcmlnaW4iOmZhbHNlLCJvcmlnaW4iOiJodHRwczovL2Z1c2lvbmF1dGguaW8iLCJ0eXBlIjoid2ViYXV0aG4uZ2V0In0=",
"signature": "MEUCIQDUwlDp9aNcYQmvpVGLJ35H8lRWjWsfjVsfPf_5HhY3GwIgahBhISBxv82ZS4ll8TZiJp5bIN2CGx_-VjUymfzKqGA=",
"userHandle": "NzAzZmUyZDItMmQzOS00Y2I3LWI3NmQtMGI5OTE4ZWQyNDU3"
},
"type": "public-key"
},
"origin": "https://auth.piedpiper.com",
"rpId": "piedpiper.com"
}The call to /api/webauthn/login completes the authentication ceremony by validating the request against the WebAuthn specification, verifying the signature, and authenticating the user. This API returns the user object for the authenticated user along with access tokens for the successful authentication.
Complete WebAuthn Authentication Response JSON
{
"token": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJleHAiOjE0ODUxNDA5ODQsImlhdCI6MTQ4NTEzNzM4NCwiaXNzIjoiYWNtZS5jb20iLCJzdWIiOiIyOWFjMGMxOC0wYjRhLTQyY2YtODJmYy0wM2Q1NzAzMThhMWQiLCJhcHBsaWNhdGlvbklkIjoiNzkxMDM3MzQtOTdhYi00ZDFhLWFmMzctZTAwNmQwNWQyOTUyIiwicm9sZXMiOltdfQ.Mp0Pcwsz5VECK11Kf2ZZNF_SMKu5CgBeLN9ZOP04kZo",
"user": {
"active": true,
"birthDate": "1976-05-30",
"connectorId": "e3306678-a53a-4964-9040-1c96f36dda72",
"data": {
"displayName": "Johnny Boy",
"favoriteColors": [
"Red",
"Blue"
]
},
"email": "example@fusionauth.io",
"expiry": 1571786483322,
"firstName": "John",
"fullName": "John Doe",
"id": "00000000-0000-0001-0000-000000000000",
"identities": [
{
"insertInstant": 1742936980069,
"lastLoginInstant": 1742936980069,
"lastUpdateInstant": 1742936980069,
"primary": true,
"type": "email",
"value": "example@fusionauth.io",
"verified": false,
"verifiedReason": "Disabled"
},
{
"insertInstant": 1742936980069,
"lastLoginInstant": 1742936980069,
"lastUpdateInstant": 1742936980069,
"primary": true,
"type": "phoneNumber",
"value": "+13035551212",
"verified": false,
"verifiedReason": "Disabled"
},
{
"displayValue": "johnny123",
"insertInstant": 1742936980069,
"lastLoginInstant": 1742936980069,
"lastUpdateInstant": 1742936980069,
"moderationStatus": "ACTIVE",
"primary": true,
"type": "username",
"value": "johnny123",
"verified": false,
"verifiedReason": "Unverifiable"
}
],
"imageUrl": "http://65.media.tumblr.com/tumblr_l7dbl0MHbU1qz50x3o1_500.png",
"insertInstant": 1742936980069,
"lastLoginInstant": 1742936980069,
"lastName": "Doe",
"middleName": "William",
"mobilePhone": "303-555-1234",
"passwordChangeRequired": false,
"passwordLastUpdateInstant": 1742936980069,
"phoneNumber": "+13035551212",
"preferredLanguages": [
"en",
"fr"
],
"registrations": [
{
"applicationId": "10000000-0000-0002-0000-000000000001",
"data": {
"displayName": "Johnny",
"favoriteSports": [
"Football",
"Basketball"
]
},
"id": "00000000-0000-0002-0000-000000000000",
"insertInstant": 1742936980069,
"lastLoginInstant": 1742936980069,
"preferredLanguages": [
"en",
"fr"
],
"roles": [
"user",
"community_helper"
],
"username": "johnny123",
"usernameStatus": "ACTIVE",
"verified": true,
"verifiedInstant": 1742936980069
}
],
"timezone": "America/Denver",
"tenantId": "f24aca2b-ce4a-4dad-951a-c9d690e71415",
"twoFactor": {
"methods": [
{
"authenticator": {
"algorithm": "HmacSHA1",
"codeLength": 6,
"timeStep": 30
},
"id": "35VW",
"method": "authenticator"
},
{
"id": "V7SH",
"method": "sms",
"mobilePhone": "555-555-5555"
},
{
"email": "example@fusionauth.io",
"id": "7K2G",
"method": "email"
}
]
},
"usernameStatus": "ACTIVE",
"username": "johnny123",
"verified": true,
"verifiedInstant": 1742936980069
}
}Completing the Assertion#
You can also complete a WebAuthn authentication ceremony by calling the /api/webauthn/assert endpoint. This endpoint performs the same request validation and signature verification as /api/webauthn/login, but it does not authenticate the user. It may be useful to validate that a user has access to passkey without authenticating them.
REQUEST_PAYLOAD='{...}'
curl -H "Content-type: application/json" https://local.fusionauth.io/api/webauthn/assert -d $REQUEST_PAYLOADComplete WebAuthn Assertion API call
Here’s an example request payload where credential is the transformedCredential from the snippet above:
Complete WebAuthn Assertion Request JSON
{
"credential": {
"id": "HdN9wqP9mqOonacmiM2gIjASFYg",
"response": {
"authenticatorData": "mPsv4VW-wth0V9gzsxWRFn-1SyC9gM4-QC4ptMFDNhUFAAAAKQ==",
"clientDataJSON": "eyJjaGFsbGVuZ2UiOiJTeTYzQldla285blFsYzVOQmVWcE1BWjFtQ0hvdzBXUXVFeDRJU2xuQzR3IiwiY3Jvc3NPcmlnaW4iOmZhbHNlLCJvcmlnaW4iOiJodHRwczovL2Z1c2lvbmF1dGguaW8iLCJ0eXBlIjoid2ViYXV0aG4uZ2V0In0=",
"signature": "MEUCIQDUwlDp9aNcYQmvpVGLJ35H8lRWjWsfjVsfPf_5HhY3GwIgahBhISBxv82ZS4ll8TZiJp5bIN2CGx_-VjUymfzKqGA=",
"userHandle": "NzAzZmUyZDItMmQzOS00Y2I3LWI3NmQtMGI5OTE4ZWQyNDU3"
},
"type": "public-key"
},
"origin": "https://auth.piedpiper.com",
"rpId": "piedpiper.com"
}The call to /api/webauthn/assert completes the authentication ceremony by validating the request against the WebAuthn specification and verifying the signature, but it does not authenticate the user. This API returns the WebAuthn passkey that was used to complete the assertion.
Complete WebAuthn Assertion Response JSON
{
"credential": {
"algorithm": -7,
"attestationType": "none",
"authenticatorSupportsUserVerification": true,
"credentialId": "HdN9wqP9mqOonacmiM2gIjASFYg",
"data": {},
"displayName": "Chrome Touch ID",
"name": "richard@fusionauth.io",
"id": "c664318a-2384-4c35-9475-9a200e1d3b72",
"insertInstant": 1668011701792,
"discoverable": false,
"lastUseInstant": 1668021630599,
"publicKey": "-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\nMFkwEwYHKoZIzj0CAQYIKoZIzj0DAQcDQgAEz9DI9AQfZn1aDJG5sw3Ckl7SoQ7E\nLPElDoJMijphvVigTcNMTc8H9Xptl8B20QHMOXGTzaUxLGNY1c8yhw9VVA==\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----",
"relyingPartyId": "piedpiper.com",
"signCount": 41,
"tenantId": "30663132-6464-6665-3032-326466613934",
"transports": [
"internal"
],
"userId": "703fe2d2-2d39-4cb7-b76d-0b9918ed2457"
}
}Customizing WebAuthn#
You can configure the FusionAuth WebAuthn implementation to meet your application’s needs in a number of ways. For details on WebAuthn workflow configuration, check out the WebAuthn Admin Guide.
Themes#
If you are using FusionAuth’s hosted login pages to present WebAuthn pages to users, you can customize those pages using a theme. There are several themed pages related to WebAuthn:
- User account self service
- List WebAuthn passkeys
- Add WebAuthn passkey
- Delete WebAuthn passkey
- OAuth
- WebAuthn bootstrap login
- WebAuthn re-authentication enable
- WebAuthn re-authentication login
Here is more information about themes.
Challenge Customization#
You can modify the lifetime of the one-time challenge generated for WebAuthn registration and authentication ceremonies. By default both are 180 seconds; change this in the tenant settings under Advanced -> External identifier durations :
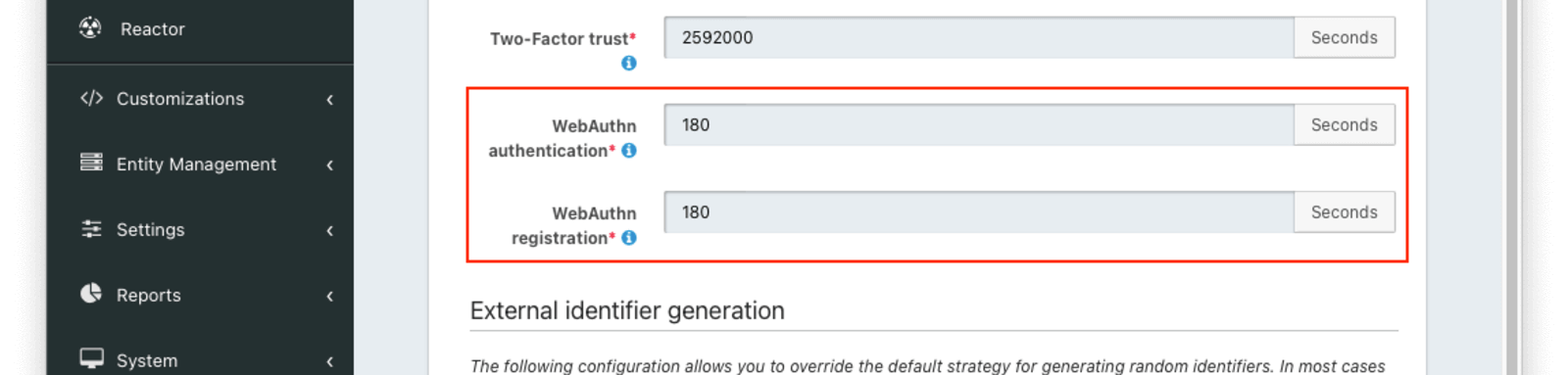
You may want to adjust the lifetime of these challenges to change how long a user has to complete a ceremony once it has been started. If an attempt is made to complete the ceremony after the challenge expires, it will fail. These values are also used as the timeout for the corresponding WebAuthn JavaScript API calls by returning the value in milliseconds as part of the /api/webauthn/register/start and /api/webauthn/start API responses. The WebAuthn JavaScript APIs treat the timeout value as a hint. The browser may allow the user more time to complete the ceremony (e.g. if the timeout is deemed too short), but FusionAuth will still expire the challenge, preventing the ceremony from being completed. The WebAuthn authentication value is used for both authentication and assertion.
Troubleshooting#
Due to the server- and client-side components of each of the WebAuthn ceremonies and compatibility depending on both the browser and operating system, troubleshooting issues can be difficult. These tips may help you when issues come up.
Browser Compatibility#
WebAuthn is now supported across a variety of web browsers, but if you experience issues, it’s worth checking whether your browser is compatible. Be sure to check the notes section for limitations based on specific authenticators or operating systems and evaluate whether you may be experiencing one of those limitations.
Secure Context#
WebAuthn can only be used in secure contexts. Briefly, this means that the browser must have a valid TLS connection for the current page. If WebAuthn is called from an iframe, then both the iframe and the embedding page must be secured.
Relying Party Id#
A WebAuthn passkey is scoped to a specific relying party Id at the time it is created. Passkeys cannot be used with a different relying party Id than they were registered, and there are restrictions on allowed relying party Ids during a WebAuthn ceremony based on the browser request origin’s effective domain.
If the relying party Id for a tenant is changed because of a configuration change or a domain change, passkeys registered prior to the change will no longer work. See the Relying Party Id section in the WebAuthn Admin Guide for more detail on constraints and configuration options.
WebAuthn JavaScript Binary Format#
As mentioned earlier in this guide, certain request and response fields on FusionAuth’s WebAuthn APIs must be encoded as base64url strings for transport over the network, but the WebAuthn JavaScript API uses JavaScript’s ArrayBuffer type for these values. See the transform sections in this guide for more information on which fields must be converted.

