Tokens
Overview
When using the OAuth2 and OpenID Connect authentication grants you’ll be dealing with some tokens. We’ll review each token type, the purpose and how to use them.
Here’s a presentation discussing how to use JWTs in a microservices architecture:
JWT Structure
With the exception of the refresh token, each token described here is a JSON Web Token (JWT) and each JWT has a header, a payload and a signature. You can decode JWTs using any number of online tools, because it’s two base 64 encoded strings joined by periods, with the signature for integrity checking.
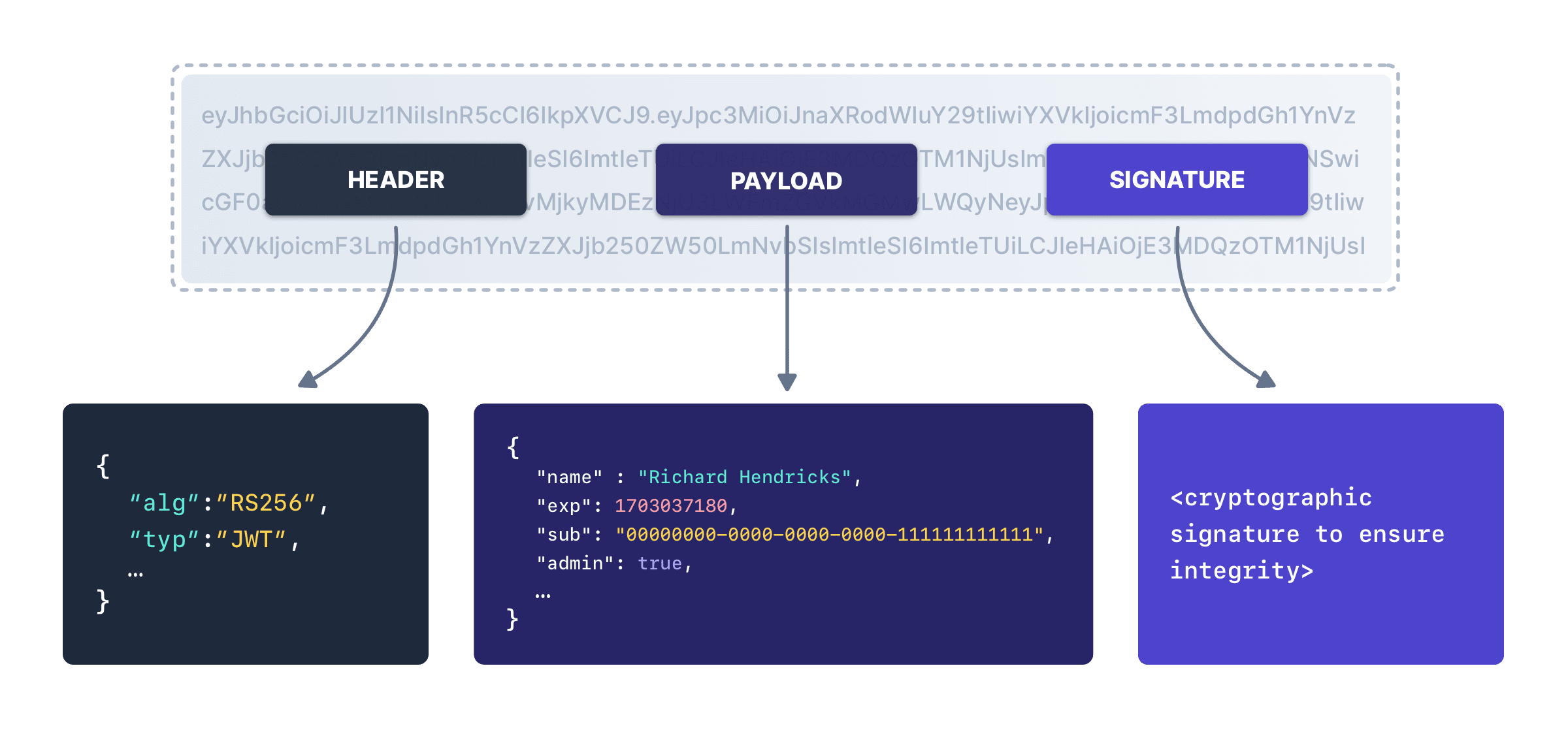
Header
The following describes the claims found in the JWT header.
gtyArray<String>Available since 1.36.0The list of grants in the order the grant occurred.
For example, if the token was the result of an authorization_code grant, the value will be [authorization_code].
If the token was generated using a refresh token using the refresh_token grant, the value will be [authorization_code, refresh_token] if the initial grant used to obtain the refresh token was the authorization_code grant.
kidStringThe unique key identifier that represents the key used to build the signature.
typStringThe type of token, this value is always JWT.
Access Token
The access token is an opaque token per the OAuth2 specification. In the FusionAuth implementation the access token is a JSON Web Token (JWT).
Access Token Claims
applicationIdUUIDThe unique Id of the Application for which the User has been authenticated. A JWT can only represent authorization to a single Application.
This claim is only present if the User has a registration to the Application.
To obtain a JWT for another Application you must either authenticate again with a different applicationId using the Authentication API or utilize the Issue a JWT API to exchange a valid JWT for another.
audStringThe audience the JWT is intended for. This registered claim is defined by RFC 7519 Section 4.1.3.
This claim will be equal to the client_id.
authenticationTypeStringThe method used to authenticate the User which resulted in this JWT being generated. The possible values are:
-
APPLE- The user was authenticated using Apple. Available since 1.17.0 -
APPLICATION_TOKEN- The user was authenticated using an Application Authentication Token. -
EpicGames- The user was authenticated using Epic Games. Available since 1.28.0 -
FACEBOOK- The user was authenticated using Facebook. Available since 1.1.0 -
FEDERATED_JWT- The user was authenticated using a JWT from an external source. -
GENERIC_CONNECTOR- The user was authenticated using a generic connector. Available since 1.18.0 -
GOOGLE- The user was authenticated using Google. Available since 1.1.0 -
HYPR- The user was authenticated using HYPR. Available since 1.12.0 -
JWT_SSO- A valid JWT associated with one application was exchanged for another JWT associated with a different application. -
LDAP_CONNECTOR- The user was authenticated using an LDAP connector. Available since 1.18.0 -
LINKEDIN- The user was authenticated using LinkedIn. Available since 1.23.0 -
Nintendo- The user was authenticated using Nintendo. Available since 1.36.0 -
ONE_TIME_PASSWORD- The user was authenticated using a one-time password. Available since 1.5.0 -
OPENID_CONNECT- The user was authenticated using OIDC. Available since 1.1.0 -
PASSWORD- The user was authenticated using a loginId and password combination. -
PASSWORDLESS- The user was authenticated using a passwordless login link. Available since 1.5.0 -
PING- The user was authenticated using aPUTrequest on the Login API. This is used to record a login event without prompting for credentials, such as when the FusionAuth SSO session is used. -
REFRESH_TOKEN- The user requested a new JWT using a refresh token. -
REGISTRATION- The user was created using the Registration API. Available since 1.16.0 -
SAMLv2- The user was authenticated using SAMLv2. Available since 1.6.0 -
SAMLv2IdpInitiated- The user was authenticated using SAMLv2 IdP Initiated login. Available since 1.28.0 -
SonyPSN- The user was authenticated using Sony. Available since 1.28.0 -
Steam- The user was authenticated using Steam. Available since 1.28.0 -
TWITTER- The user was authenticated using Twitter. Available since 1.1.0 -
Twitch- The user was authenticated using Twitch. Available since 1.28.0 -
USER_CREATE- The user was created using the User API. Available since 1.16.0 -
WebAuthn- The user was authenticated using a passkey. Available since 1.41.0 -
Xbox- The user was authenticated using Xbox. Available since 1.28.0
auth_timeLongAvailable since 1.36.0The time of the initial authentication request, expressed as UNIX time which is the number of seconds since Epoch. This claim will remain the same even when the token has been re-issued through the use of a Refresh Token.
emailStringThe email address of the User whose claims are represented by this JWT.
Removed in 1.50.0In version 1.50.0 and later this claim is not returned when the oauthConfiguration.scopeHandlingPolicy value of the Application is Strict.
email_verifiedBooleanThe OpenId Connect claim indicating if the User’s email has been verified.
Removed in 1.50.0In version 1.50.0 and later this claim is not returned when the oauthConfiguration.scopeHandlingPolicy value of the Application is Strict.
expLongThe expiration instant of the JWT, expressed as UNIX time which is the number of seconds since Epoch. This registered claim is defined by RFC 7519 Section 4.1.4.
iatLongThe instant that the JWT was issued, expressed as UNIX time which is the number of seconds since Epoch. This registered claim is defined by RFC 7519 Section 4.1.6.
jtiStringAvailable since 1.18.0The unique identifier for this JWT. This registered claim is defined by RFC 7519 Section 4.1.7.
issStringThe issuer of the JWT. For FusionAuth, this is always the value defined in the tenant JWT configuration. This registered claim is defined by RFC 7519 Section 4.1.1.
preferred_usernameStringAvailable since 1.5.0The username of the User whose claims are represented by this JWT.
Removed in 1.50.0In version 1.50.0 and later this claim is not returned when the oauthConfiguration.scopeHandlingPolicy value of the Application is Strict.
rolesArray<String>The roles assigned to the User in the authenticated Application. This claim is only present if the User has a registration to the Application.
scopeStringAvailable since 1.50.0The scope of the Access token. This meaning of this field is specified by RFC 6749 Section 3.3.
Contains the validated and consented OAuth scopes from the initial authentication request. See Scopes for more detail on scope consent.
sidStringAvailable since 1.37.0The unique Id of the refresh token returned along with this access token when the offline_access scope was requested. This unique Id is the persistent identifier for this refresh token, and will not change even when using one-time use refresh tokens. This value may optionally be used to revoke the token using the Refresh Token API.
subUUIDThe subject of the access token. This value is equal to the User’s unique Id in FusionAuth. This registered claim is defined by RFC 7519 Section 4.1.2.
tidUUIDAvailable since 1.36.0The FusionAuth Tenant unique Id.
Sample Access Token
Here’s a sample access token.
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCIsImd0eSI6WyJhdXRob3JpemF0aW9uX2NvZGUiXSwia2lkIjoiWG9xN2tLM2VJWHJ5WW1pNTBaT3ZnMmJjY2VNIn0.eyJhdWQiOiJlOWZkYjk4NS05MTczLTRlMDEtOWQ3My1hYzJkNjBkMWRjOGUiLCJleHAiOjE3MDMwMzcxODAsImlhdCI6MTcwMzAzMzU4MCwiaXNzIjoiYWNtZS5jb20iLCJzdWIiOiIwMDAwMDAwMC0wMDAwLTAwMDAtMDAwMC0xMTExMTExMTExMTEiLCJqdGkiOiIyZTIyNzFkNy0zMDU3LTRiZmQtOTlhYi0zNGFmNDhlODQ1NjciLCJhdXRoZW50aWNhdGlvblR5cGUiOiJQQVNTV09SRCIsImVtYWlsIjoicmljaGFyZEBleGFtcGxlLmNvbSIsImVtYWlsX3ZlcmlmaWVkIjp0cnVlLCJhcHBsaWNhdGlvbklkIjoiZTlmZGI5ODUtOTE3My00ZTAxLTlkNzMtYWMyZDYwZDFkYzhlIiwic2NvcGUiOiJvZmZsaW5lX2FjY2VzcyBwcm9maWxlIG9wZW5pZCIsInJvbGVzIjpbXSwic2lkIjoiMGFiZTcxMzktMGJkMC00ZmQwLWE0NTAtYzFlOGIxNmU3MTBhIiwiYXV0aF90aW1lIjoxNzAzMDMzNTgwLCJ0aWQiOiJkN2QwOTUxMy1hM2Y1LTQwMWMtOTY4NS0zNGFiNmM1NTI0NTMifQ.IyQL-d2BgG0VmfHg2gmge7MgDwYXrMX7xDv5lz-pe0oravlZUAt0B9DhfPaY-EFZ0Dus95dTIVtU4-THYkGNy4Un21FjoTAGU8fZK_Cew16814194WvQDR5wL_cZymog9UmmUv_owKot5YzwLdoJKXVBI7CgM3c43KrwGOdFPMHNkL-YHQgWFQzXBfRpmdu45K56Np8mYVbgVwFKgRXRIGy0PpBGaoeRiN1DfeB3fzR944ddActyOfTVovIXqO7O5HORS8vFQA6h1wpNdAtrbCMqHEVgQWHSMZCkUGM7RlE3V9WepRcaLkpuMocQfxDasoRZCIeK1ZwRHuSbAh7zFAClient Credentials Access Token
The access token is an opaque token per the OAuth2 specification. In the FusionAuth implementation, the credentials access token is a JSON Web Token (JWT).
Available since version 1.26.
Client Credentials Access Token Claims
audStringThe audience of this token. This value is equal to the target Entity’s unique Id in FusionAuth. This registered claim is defined by RFC 7519 Section 4.1.3.
expLongThe expiration instant of the JWT expressed as UNIX time, which is the number of seconds since Epoch. This registered claim is defined by RFC 7519 Section 4.1.4.
iatLongThe instant that the JWT was issued expressed as UNIX time, which is the number of seconds since Epoch. This registered claim is defined by RFC 7519 Section 4.1.6.
jtiStringThe unique identifier for this JWT. This registered claim is defined by RFC 7519 Section 4.1.7.
issStringThe issuer of the JWT. For FusionAuth, this is always the value defined in the tenant JWT configuration. This registered claim is defined by RFC 7519 Section 4.1.1.
permissionsArray<String>The permission granted to the recipient Entity by the target Entity. This claim is only present if permissions are associated with the grant and any requested permissions are found in the grant.
scopeStringThe scope of the Access token. This meaning of this field is specified by RFC 6749 Section 3.3 and referenced in Client Credentials Grant RFC 6749 Section 4.4
Valid scopes are described in the client credentials scopes section.
subUUIDThe subject of the access token. This value is equal to the recipient Entity’s unique Id in FusionAuth. This registered claim is defined by RFC 7519 Section 4.1.2.
tidUUIDAvailable since 1.36.0The FusionAuth Tenant unique Id.
Id Token
The Id Token is part of the OpenID Connect specification. The Id Token is a JSON Web Token (JWT) per the OpenID Connect specification. The Id Token is similar to the access token in the FusionAuth implementation. The Id Token may contain additional claims not present in the Access Token.
The Id Token may be returned as part of an Authentication request when the openid scope is requested.
In version 1.50.0 and later the Id Token claims are populated based on the requested OAuth scopes when the oauthConfiguration.scopeHandlingPolicy value of the application object is Strict.
Id Token Claims
applicationIdUUIDThe unique Id of the Application for which the User has been authenticated. A JWT can only represent authorization to a single Application.
This claim is only present if the User has a registration to the Application.
To obtain a JWT for another Application you must either authenticate again with a different applicationId using the Authentication API or utilize the Issue a JWT API to exchange a valid JWT for another.
As of version 1.24.0, this claim is no longer returned by default. The id_token should not be utilized for authorization, so this claim was removed to make it less likely for a holder of this token to incorrectly utilize this token. If you have a need for this claim, it can be added back using a JWT populate lambda.
at_hashStringAvailable since 1.5.0The Access Token hash value. As defined by the 3.1.3.6 of the OpenID Connect Core specification this value is a base64 encoded hash of the access token.
audStringThe audience the JWT is intended for. This registered claim is defined by RFC 7519 Section 4.1.3.
This claim will be equal to the client_id.
authenticationTypeStringThe method used to authenticate the User which resulted in this JWT being generated. The possible values are:
-
APPLE- The user was authenticated using Apple. Available since 1.17.0 -
APPLICATION_TOKEN- The user was authenticated using an Application Authentication Token. -
EpicGames- The user was authenticated using Epic Games. Available since 1.28.0 -
FACEBOOK- The user was authenticated using Facebook. Available since 1.1.0 -
FEDERATED_JWT- The user was authenticated using a JWT from an external source. -
GENERIC_CONNECTOR- The user was authenticated using a generic connector. Available since 1.18.0 -
GOOGLE- The user was authenticated using Google. Available since 1.1.0 -
HYPR- The user was authenticated using HYPR. Available since 1.12.0 -
JWT_SSO- A valid JWT associated with one application was exchanged for another JWT associated with a different application. -
LDAP_CONNECTOR- The user was authenticated using an LDAP connector. Available since 1.18.0 -
LINKEDIN- The user was authenticated using LinkedIn. Available since 1.23.0 -
Nintendo- The user was authenticated using Nintendo. Available since 1.36.0 -
ONE_TIME_PASSWORD- The user was authenticated using a one-time password. Available since 1.5.0 -
OPENID_CONNECT- The user was authenticated using OIDC. Available since 1.1.0 -
PASSWORD- The user was authenticated using a loginId and password combination. -
PASSWORDLESS- The user was authenticated using a passwordless login link. Available since 1.5.0 -
PING- The user was authenticated using aPUTrequest on the Login API. This is used to record a login event without prompting for credentials, such as when the FusionAuth SSO session is used. -
REFRESH_TOKEN- The user requested a new JWT using a refresh token. -
REGISTRATION- The user was created using the Registration API. Available since 1.16.0 -
SAMLv2- The user was authenticated using SAMLv2. Available since 1.6.0 -
SAMLv2IdpInitiated- The user was authenticated using SAMLv2 IdP Initiated login. Available since 1.28.0 -
SonyPSN- The user was authenticated using Sony. Available since 1.28.0 -
Steam- The user was authenticated using Steam. Available since 1.28.0 -
TWITTER- The user was authenticated using Twitter. Available since 1.1.0 -
Twitch- The user was authenticated using Twitch. Available since 1.28.0 -
USER_CREATE- The user was created using the User API. Available since 1.16.0 -
WebAuthn- The user was authenticated using a passkey. Available since 1.41.0 -
Xbox- The user was authenticated using Xbox. Available since 1.28.0
auth_timeLongAvailable since 1.36.0The time of the initial authentication request expressed as UNIX time which is the number of seconds since Epoch. This claim will remain the same even when the token has been re-issued through the use of a Refresh Token.
birthdateStringAvailable since 1.50.0The birthDate of the User if available.
Format will be in YYYY-MM-DD as defined by the OpenID Connect core specification.
When the Scope handling policy is Strict, this field is only populated when the scope claim contains the profile scope.
c_hashStringAvailable since 1.5.0The Authorization Code hash value. As defined by the 3.3.2.11 of the OpenID Connect Core specification this value is an encoded hash of the authorization code, the algorithm used to generate this hash depends upon the algorithm used to generate the id_token signature.
emailStringThe email address of the User whose claims are represented by this JWT.
In version 1.50.0 and later, when the Scope handling policy is Strict, this field is only populated when the scope claim contains the email scope.
email_verifiedBooleanThe OpenId Connect claim indicating if the User’s email has been verified.
In version 1.50.0 and later, when the Scope handling policy is Strict, this field is only populated when the scope claim contains the email scope.
expLongThe expiration instant of the JWT, expressed as UNIX time which is the number of seconds since Epoch. This registered claim is defined by RFC 7519 Section 4.1.4.
family_nameStringAvailable since 1.50.0The last name of the User if available.
When the Scope handling policy is Strict, this field is only populated when the scope claim contains the profile scope.
given_nameStringAvailable since 1.50.0The first name of the User if available.
When the Scope handling policy is Strict, this field is only populated when the scope claim contains the profile scope.
iatLongThe instant that the JWT was issued, expressed as UNIX time which is the number of seconds since Epoch. This registered claim is defined by RFC 7519 Section 4.1.6.
issStringThe issuer of the JWT. For FusionAuth, this is always the value defined in the tenant JWT configuration. This registered claim is defined by RFC 7519 Section 4.1.1.
jtiStringAvailable since 1.18.0The unique identifier for this JWT. This registered claim is defined by RFC 7519 Section 4.1.7.
middle_nameStringAvailable since 1.50.0The middle name of the User if available.
When the Scope handling policy is Strict, this field is only populated when the scope claim contains the profile scope.
nameStringAvailable since 1.50.0The full name of the User if available.
When the Scope handling policy is Strict, this field is only populated when the scope claim contains the profile scope.
nonceStringAvailable since 1.5.0phone_numberStringAvailable since 1.50.0The phone number of the User if available.
When the Scope handling policy is Strict, this field is only populated when the scope claim contains the phone scope.
pictureStringAvailable since 1.50.0A URL to a picture of the User if available.
When the Scope handling policy is Strict, this field is only populated when the scope claim contains the profile scope.
preferred_usernameStringAvailable since 1.5.0The username of the User whose claims are represented by this JWT.
In version 1.50.0 and later, when the Scope handling policy is Strict, this field is only populated when the scope claim contains the profile scope.
rolesArray<String>DEPRECATEDThe roles assigned to the User in the authenticated Application. This claim is only present if the User has a registration to the Application.
Removed in 1.24.0As of version 1.24.0, this claim is no longer returned by default. The id_token should not be utilized for authorization, so this claim was removed to make it less likely for a holder of this token to incorrectly utilize this token. If you have a need for this claim, it can be added back using a JWT populate lambda.
scopeStringAvailable since 1.50.0The scope of the Id Token. This meaning of this field is specified by RFC 6749 Section 3.3.
Contains the validated and consented OAuth scopes from the initial authentication request. See Scopes for more detail on scope consent.
sidStringThe SSO session Id. This claim will only be present when this token is produced using an interactive grant during a single-signon request such as the Authorization Code grant or the Implicit grant.
subUUIDThe subject of the Id Token. This value is equal to the User’s unique Id in FusionAuth. This registered claim is defined by RFC 7519 Section 4.1.2.
tidUUIDAvailable since 1.36.0The FusionAuth Tenant unique Id.
Sample Id Token
Here’s a sample Id token.
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCIsImd0eSI6WyJhdXRob3JpemF0aW9uX2NvZGUiXSwia2lkIjoiWG9xN2tLM2VJWHJ5WW1pNTBaT3ZnMmJjY2VNIn0.eyJhdWQiOiJlOWZkYjk4NS05MTczLTRlMDEtOWQ3My1hYzJkNjBkMWRjOGUiLCJleHAiOjE3MDMwMzcxODAsImlhdCI6MTcwMzAzMzU4MCwiaXNzIjoiYWNtZS5jb20iLCJzdWIiOiIwMDAwMDAwMC0wMDAwLTAwMDAtMDAwMC0xMTExMTExMTExMTEiLCJqdGkiOiIyOWVkMjA5NC1jOWIxLTRmMGQtODc4Mi00YTc2NWI4YTZmOTIiLCJhdXRoZW50aWNhdGlvblR5cGUiOiJQQVNTV09SRCIsImVtYWlsIjoicmljaGFyZEBleGFtcGxlLmNvbSIsImVtYWlsX3ZlcmlmaWVkIjp0cnVlLCJhdF9oYXNoIjoiZmtqUzc4YjhCbXRlM2lRRVBIRUk2ZyIsImNfaGFzaCI6ImlrT3lkdmljUHRqNU9HMm5zcExtOFEiLCJzY29wZSI6Im9mZmxpbmVfYWNjZXNzIHByb2ZpbGUgb3BlbmlkIiwic2lkIjoiNjlhOTQ4OTYtNjg3ZS00MDQ5LTkwZGItMTY0ZDYwYWVmN2I2IiwiYXV0aF90aW1lIjoxNzAzMDMzNTgwLCJ0aWQiOiJkN2QwOTUxMy1hM2Y1LTQwMWMtOTY4NS0zNGFiNmM1NTI0NTMifQ.rT7Q39-RFT63aw996v0zu2vwS-RIYRvTccmEi_rGV19aKnRnlZD7Bx_dJaaoZxyvD3xfO1wVA2aO_nHQmKhwLuFIt4Jae0Z4a3nlJLKaumCxh4yB4vjAvKAwvhClwWYhx1LbbMl0lvVy-qvs-niVTgPLTVMYnSFXnfTuN8LMDCf7keP3SjS1MTyEeG2WtZzvPd6j2zu66rl5y3uCfpqaLbR0URDsJjQE4GbUMf7UODhZ1_ztGXg_-vGKvpomGB0-0vUmcrqXENtXRFy9hPYHXGp4T-uAy93DUo7AvsrECAHryWq6wzbLIXXeMcCpjWl87Cqb0TwMyM5D30VH2crlLQRefresh Token
The refresh token is an opaque token that is used to “refresh”, or obtain a new access token. Because the life of an access token is generally measured in minutes, the Refresh Token is by comparison a long lived token that can be used to maintain access to a protected resource.
A refresh token is associated with the same set of validated and consented OAuth scopes from the initial authentication request. The Refresh Token Grant Request can include a subset of the original scopes to request a new token with a narrower scope.
To request a refresh token during authentication you must provide the offline_access scope. The refresh token is not supported by the Implicit Grant, so if you provide the offline_access scope during an Implicit Grant workflow it will be ignored.
If you request the offline_access scope and an Refresh Token is not returned, ensure that the FusionAuth application has been configured to generate refresh tokens. Ensure Generate refresh tokens is enabled in your application settings. See Settings -> Applications -> OAuth . This setting will cause a Refresh Token to be returned when the offline_access scope is requested. You will also want to ensure the Refresh Token grant is enabled which allows the use of the Refresh Token to be exchanged for a new Access Token.
Sample Refresh Token
Here’s a sample refresh token.
ze9fi6Y9sMSf3yWp3aaO2w7AMav2MFdiMIi2GObrAi-i3248oo0jTQ
