Migrate From Supabase
Overview
This document will help you migrate off of Supabase and onto FusionAuth.
This guide assumes you have installed FusionAuth. If you have not, please view our installation guides and install FusionAuth before you begin. For more general migration information, please view the FusionAuth migration guide.
There are a number of different ways applications can be integrated with Supabase, and it would be difficult to cover them all. This guide mentions the typical parts of a bulk migration and focuses on migrating user data from a Supabase-managed user database into FusionAuth.
Planning Considerations
Obtaining User Data
You can write a custom psql script in the Supabase SQL Editor to export user data as JSON that you can import to FusionAuth. In Supabase, user data is stored in the auth.users table, and you can join the query with data from other auth tables to pull specific attributes.
Mapping User Attributes
The attributes of the User object in FusionAuth are well documented.
If there is an attribute in your user which cannot be directly mapped to a FusionAuth attribute, you can place it in the user.data field. This field can store arbitrary JSON values and will be indexed and searchable.
Social Logins
Supabase also provides integrations with other social login providers such as Twitter, Google or Facebook. Review the supported FusionAuth Identity Providers to ensure your social providers are supported.
If not supported explicitly, a provider may work with an OIDC or SAML connection. Otherwise, please open a feature request.
Migrating users with social logins such as Apple or Facebook requires that you have an existing user Id for that provider. What this unique user Id looks like depends on the particular social identity provider. The unique Id may be an email address, an integer, UUID, or a random string.
Configure the appropriate FusionAuth Identity Provider with the same values (client_id, etc) as the original user management system you are migrating away from.
Import users with the Import API, assigning each user with a social login a random password such as a UUID.
Your next step depends on whether the social login provider’s unique identifier is available as part of your migration data. If you have the social login provider’s unique identifier, for each user, use the Link API to create a link with the appropriate User Id, Identity Provider Id, and Identity Provider User Id.
- The User Id is the Id of the recently created FusionAuth User.
- The Identity Provider Id is found on the corresponding Identity Provider API documentation. Look for identityProvider.id .
- The Identity Provider User Id is the existing social provider user identifier exported or otherwise extracted from the original system.
You do not need to migrate the social network token, which may or may not be accessible. During the first login of a newly migrated user, FusionAuth finds the unique user in the social login provider based on the migrated Identity Provider User Id, and completes the login. During this process, FusionAuth stores a token on the Link, if the social provider returns one. Depending on the configuration of the social provider, users may see a prompt asking if they want to allow FusionAuth to have access to user data such as email address.
IdP linking strategies have been available since version 1.28.0. Before that version, users were linked on email.
If you do not have the social login provider’s identifier, you need to decide if you want to transparently link the two accounts, which is easier for the end user, or if you want to ask the user to manually link the accounts, which is more accurate, but may be confusing.
To transparently link the accounts, choose a linking strategy of Link On Email or Link On Username, which will create the user if they don’t exist. However, if the user has an email address at their social provider which differs from the email address that was used to sign up for your application and which you imported to FusionAuth, then two accounts will be created.
For example, if the user has a Google account richard@gmail.com, but signed up for your application with richard@fusionauth.io, then if you use the Link On Email strategy, two different accounts will be created, since FusionAuth is trying to match on email address and they don’t. The same holds true for usernames with the Link on Username strategy.
To prompt the user to link the accounts, choose a linking strategy of Pending, which will prompt the end user to sign into FusionAuth after they sign into the social provider, authoritatively linking the two accounts.
Here’s more information about IdP Linking Strategies.
Apple only returns a user’s full name the first time the user logs in. Since you have users who have already used Apple to log in to your previous authentication gateway, Apple will not provide the user’s name when they log in to FusionAuth now. The only solution is to import the user’s name manually from your previous database into FusionAuth.
Other Entities
There are often other important entities, such as connections or roles, that need to be migrated. There are usually fewer of these, so an automated migration may not make sense, but plan to move this configuration somehow.
Be aware that functionality may not be the same between Supabase and FusionAuth. This is different from user data; as long as you can somehow migrate a login identifier (a username or email) and a password hash, a user will be authenticated and successfully migrated. You can download FusionAuth before you begin a migration and build a proof of concept to learn more about the differences.
A partial list of what may need to be migrated for your application to work properly includes the following:
- In Supabase, sign-in providers are a source of data for users. FusionAuth calls these Identity Providers.
- Projects are a high-level construct that groups entities such as users and applications together. FusionAuth calls these Tenants.
- Supabase has other products your applications might be using, like Edge functions. FusionAuth does not have equivalents for these products, and is focused only on authentication.
Identifiers
When creating an object with the FusionAuth API, you can specify the Id. It must be a UUID.
This works for users, applications, and tenants, among others.
Supabase uses a custom UUID format. When migrating, a new UUID will be created for the user on FusionAuth.
If you have external dependencies on an Id stored in Supabase, you can add a new attribute under user.data (such as user.data.originalId) with the value of the Supabase Id. Because everything under user.data is indexed and available via search, you’ll be able to find your users using either the new FusionAuth Id, or the original Supabase one.
Exporting Users
To export users from Supabase, you’ll perform the following steps:
- Access the Supabase SQL Editor and create a new query.
- Paste the
ufn_get_user_migration_data_json()function code into the editor. - Run the function in the editor and save the JSON data to a file, for example,
users.json.
The script below is a user-defined psql function for exporting user data from Supabase. The script will generate a JSON array object.
Supabase user data export function
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION ufn_get_user_migration_data_json()
RETURNS table (j json) AS
$$
BEGIN
RETURN QUERY
SELECT array_to_json(array_agg(json_strip_nulls(row_to_json(r))))
FROM
(SELECT
u.instance_id,
u.encrypted_password,
EXTRACT(EPOCH from u.created_at)*1000 as created_at,
i.provider,
i.email,
CASE WHEN u.encrypted_password = '' THEN i.provider||'|'||i.user_id
ELSE 'auth0'||'|'||i.user_id
END as "user_id",
CASE WHEN u.encrypted_password = '' THEN null
ELSE substring(u.encrypted_password,5,2)
END as "factor",
substring(u.encrypted_password,8,22) as salt,
CASE WHEN u.encrypted_password = '' THEN 'hasprovider'
ELSE substring(u.encrypted_password,30,31)
END as "password",
CASE WHEN u.encrypted_password = '' THEN null
ELSE 'bcrypt'
END as "encryptionScheme",
true as email_verified
FROM auth.users u JOIN auth.identities i
ON u.id = i.user_id
) r;
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
SELECT "ufn_get_user_migration_data_json"() as "User Migration Data";The function ufn_get_user_migration_data_json() returns a JSON array with formatted user data. Create a new file on your machine, for example, users.json, and copy the generated JSON to it. You’ll upload this data to FusionAuth later.
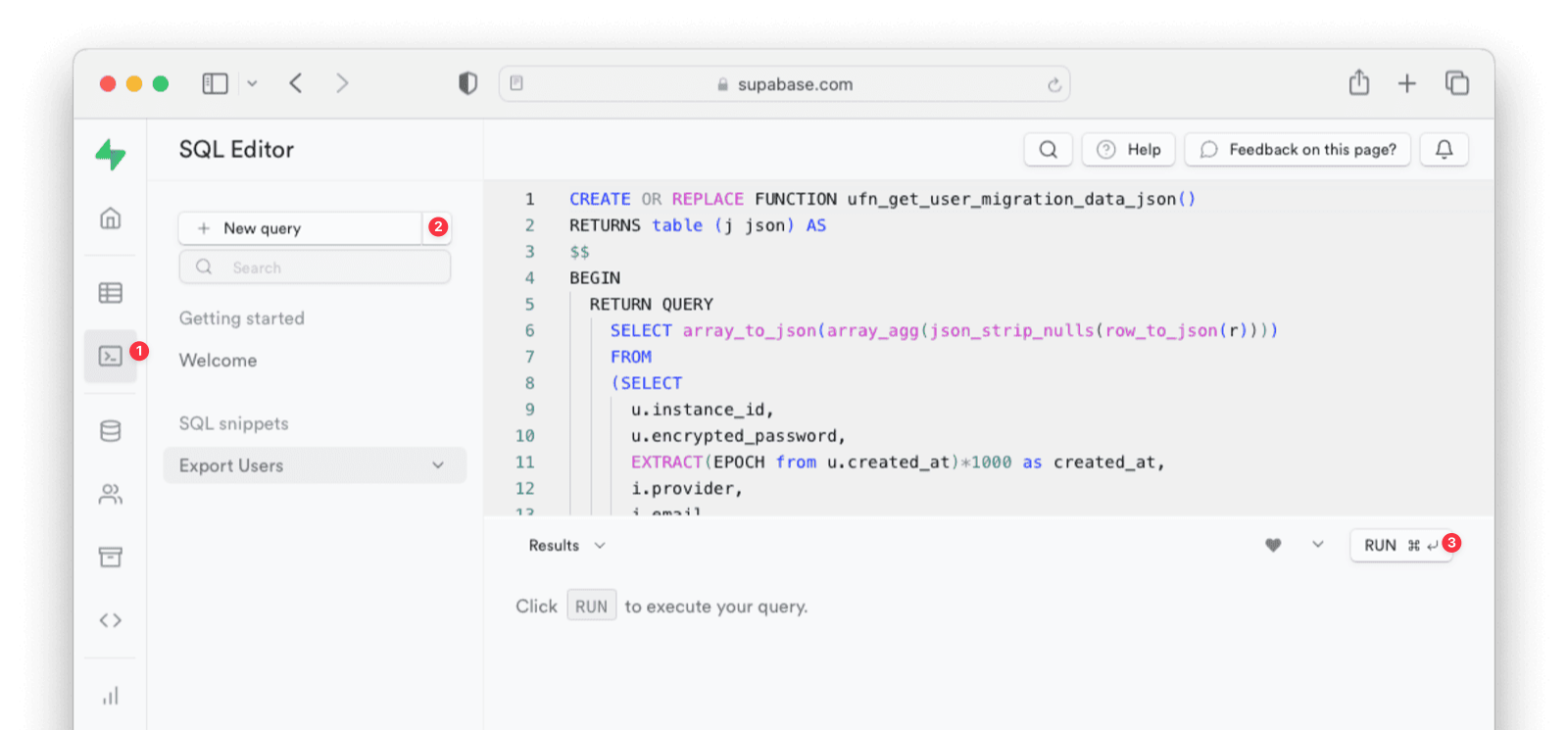
The user data to be exported will be selected from the auth table. If you have other tables that contain user-specific fields (for example, usernames), you can edit the script above to cater to that.
The JSON output produced by the script should look something like this:
[
{
"instance_id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000",
"encrypted_password": "",
"created_at": 1684248249840.815,
"provider": "facebook",
"email": "erlich@example.com",
"user_id": "facebook|99af46c2-b9e9-4471-81fd-35bdf12957aa",
"salt": "",
"password": "hasprovider",
"email_verified": true
},
{
"instance_id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000",
"encrypted_password": "$2a$10$VnxRmsfGTooc.Yy7Ez7L7.bkdHaSzseGwHkjvxZUGaGo5k4XIfDYe",
"created_at": 1684096920263.688,
"provider": "email",
"email": "richard@example.com",
"user_id": "auth0|b60d3ece-2c59-43d0-acf1-632fdefb6a54",
"factor": "10",
"salt": "VnxRmsfGTooc.Yy7Ez7L7.",
"password": "bkdHaSzseGwHkjvxZUGaGo5k4XIfDYe",
"encryptionScheme": "bcrypt",
"email_verified": true
},
{
"instance_id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000",
"encrypted_password": "",
"created_at": 1684269308911.086,
"provider": "google",
"email": "bertram@example.com",
"user_id": "google|1a5347be-4bab-4113-aaf5-51d358fd4165",
"salt": "",
"password": "hasprovider",
"email_verified": true
},
{
"instance_id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000",
"encrypted_password": "$2a$10$X06hVD7/522iK698AxX1u.NINSImp/Md75dY/yz5sYjpmGF/5aeM6",
"created_at": 1684052197215.207,
"provider": "email",
"email": "jared@example.com",
"user_id": "auth0|90d5cfea-e41e-44ea-a3bd-e16d112622f8",
"factor": "10",
"salt": "X06hVD7/522iK698AxX1u.",
"password": "NINSImp/Md75dY/yz5sYjpmGF/5aeM6",
"encryptionScheme": "bcrypt",
"email_verified": true
}
]Importing Users
Next up, import the user data. Here are the steps you need to take.
- Set Up FusionAuth
- Get the Script
- Install Needed Gems
- Use the Script
- Verify the Import
- The Final Destination of Imported Users
Set Up FusionAuth
You need to set up FusionAuth so migrated user data can be stored. As mentioned above, this guide assumes you have FusionAuth installed.
If you don’t, view our installation guides and install it before proceeding further.
Create a Test Tenant
It is best to create a separate tenant for migration testing. Tenants logically isolate configuration settings and users. If a migration goes awry or you need to redo it after tweaking settings, you can delete the test tenant and start with a clean system. To add a tenant, navigate to Tenants and choose the Add button (green plus sign).
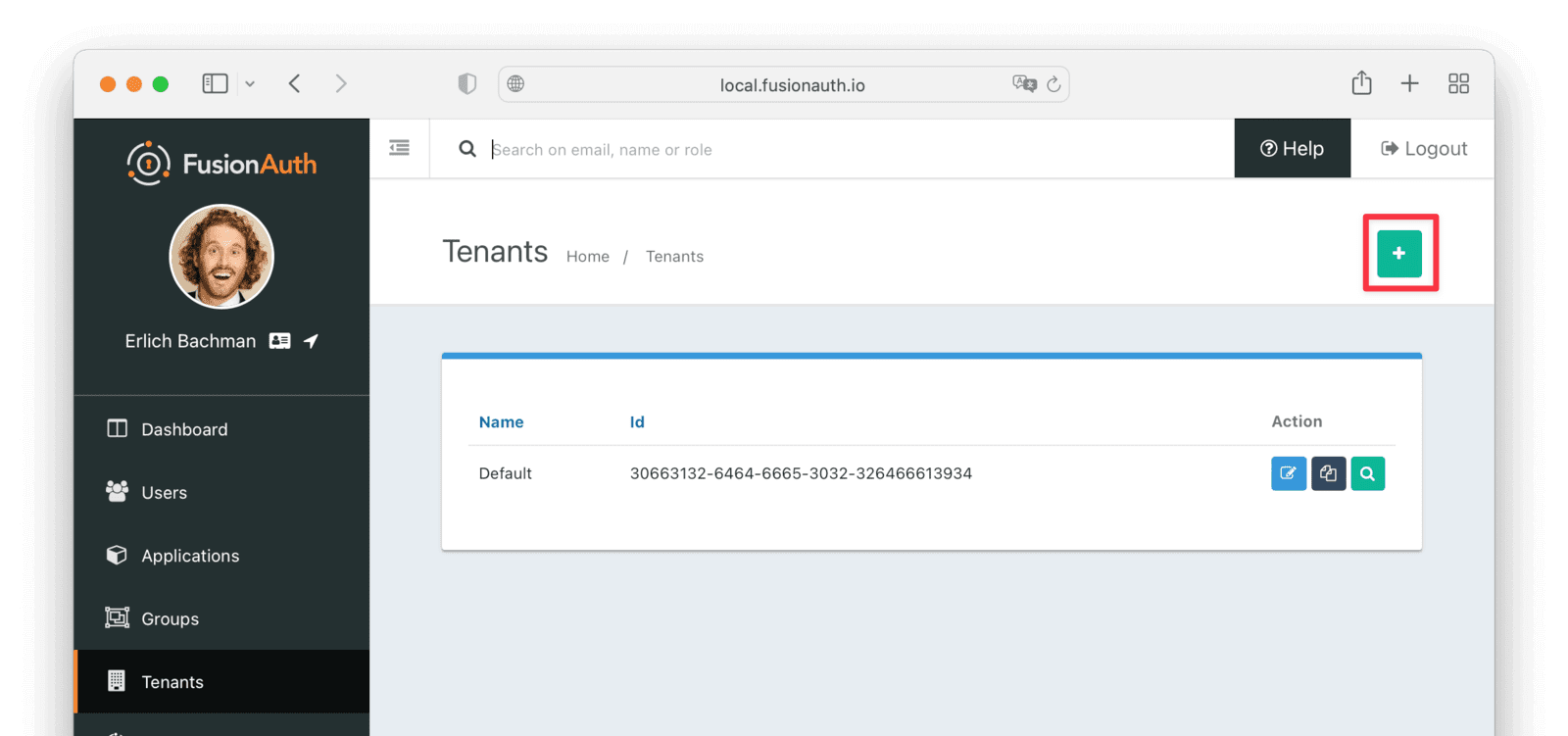
Give it a descriptive Name like Supabase import test. You shouldn’t need to modify any of the other configuration options to test importing users.
Save the tenant.
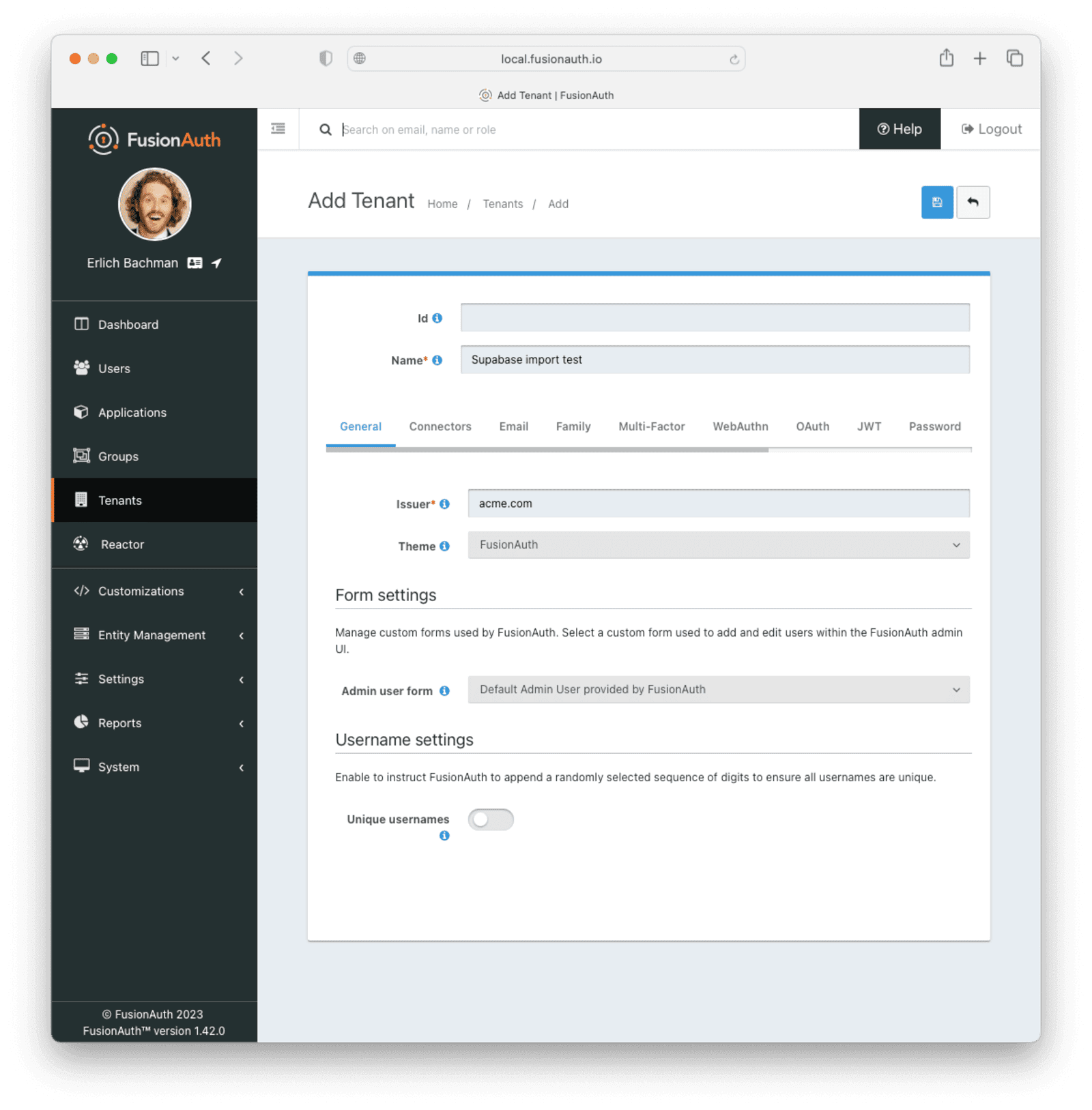
Record the Id of the tenant, which will be a UUID. It will look something like 25c9d123-8a79-4edd-9f76-8dd9c806b0f3. You’ll use this later.
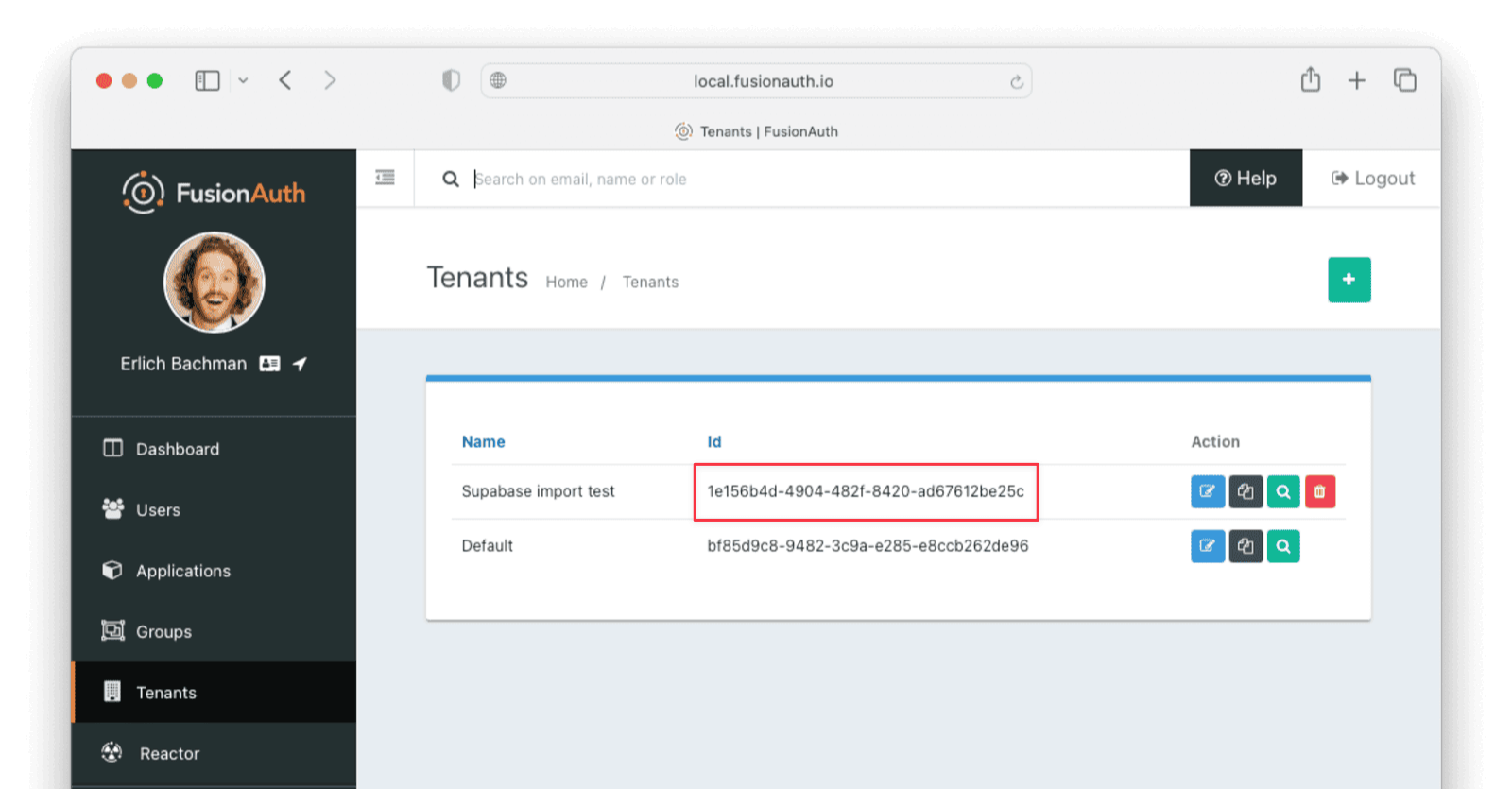
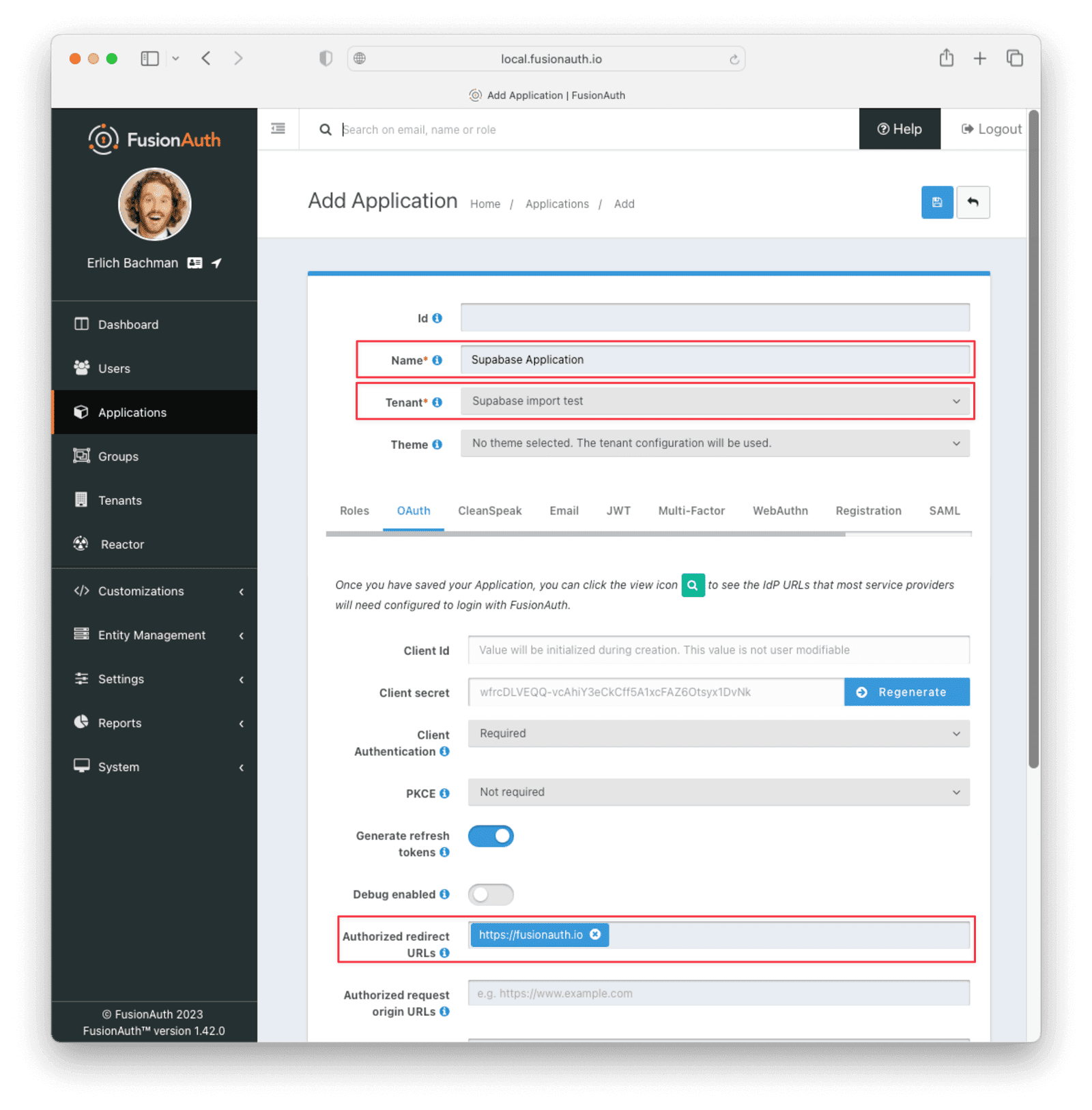
Create a Test Application
Applications are anything a user can log in to. In FusionAuth there’s no differentiation between web applications, SaaS applications, APIs and native apps. To add an application, navigate to Applications and click on the Add button (the green plus sign). Give the application a descriptive name like Supabase application.
Select your new tenant, created above, in the dropdown for the Tenant field.
Navigate to the OAuth tab and add an entry to Authorized redirect URLs . Use a dummy value such as https://example.com. Later, you’ll need to update this to be a valid redirect URL that can take the authorization code and exchange it for a token. Learn more about this in the FusionAuth OAuth documentation.
You shouldn’t need to modify any of the other configuration options to test importing users. Save the application.
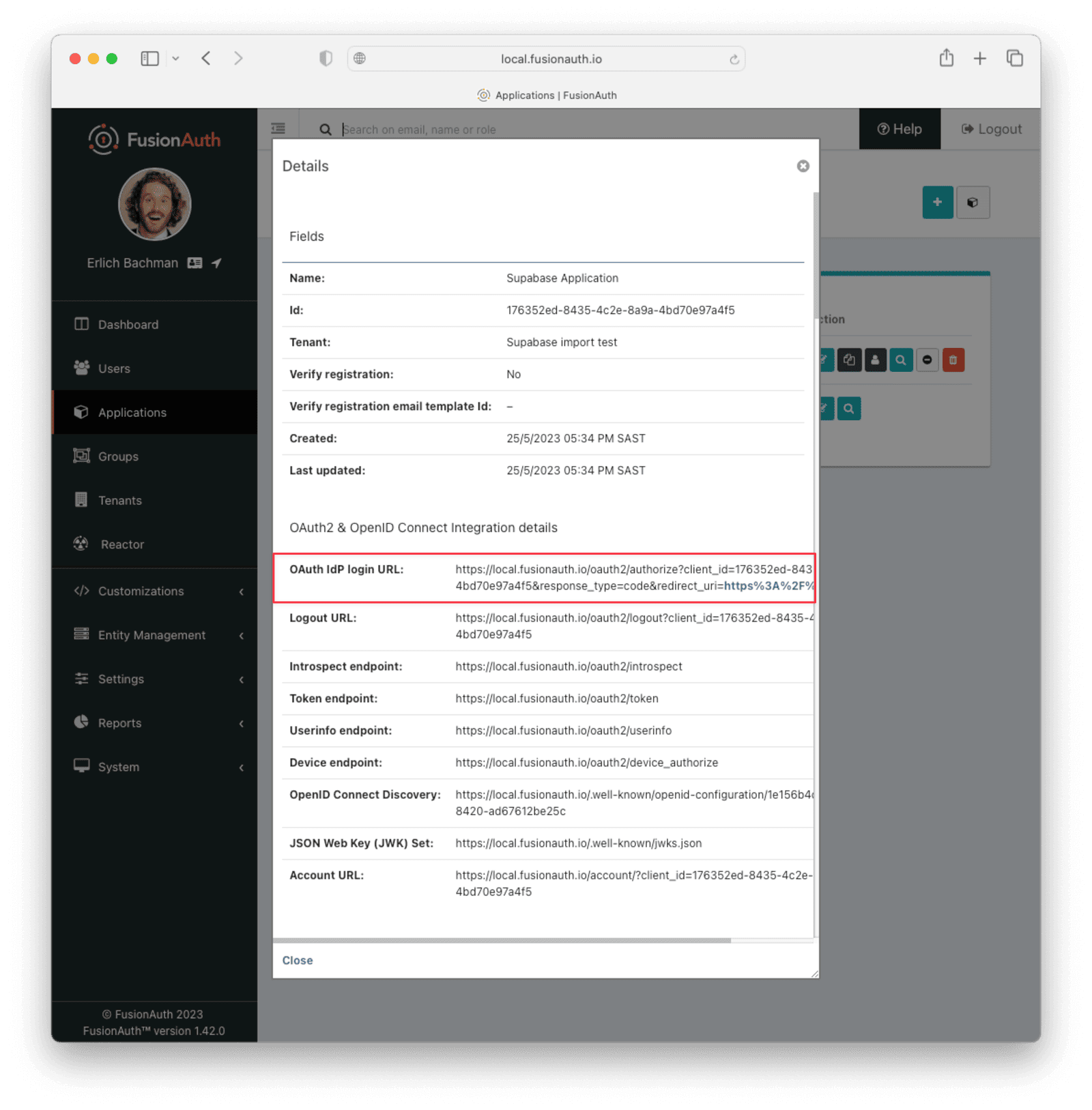
Next, view the application by clicking the green magnifying glass and note the OAuth IdP login URL . You’ll be using it to test that users can log in.
Add an API Key
The next step is to create an API key. This will be used by the import script. To do so, navigate to Settings -> API Keys in the administrative user interface.
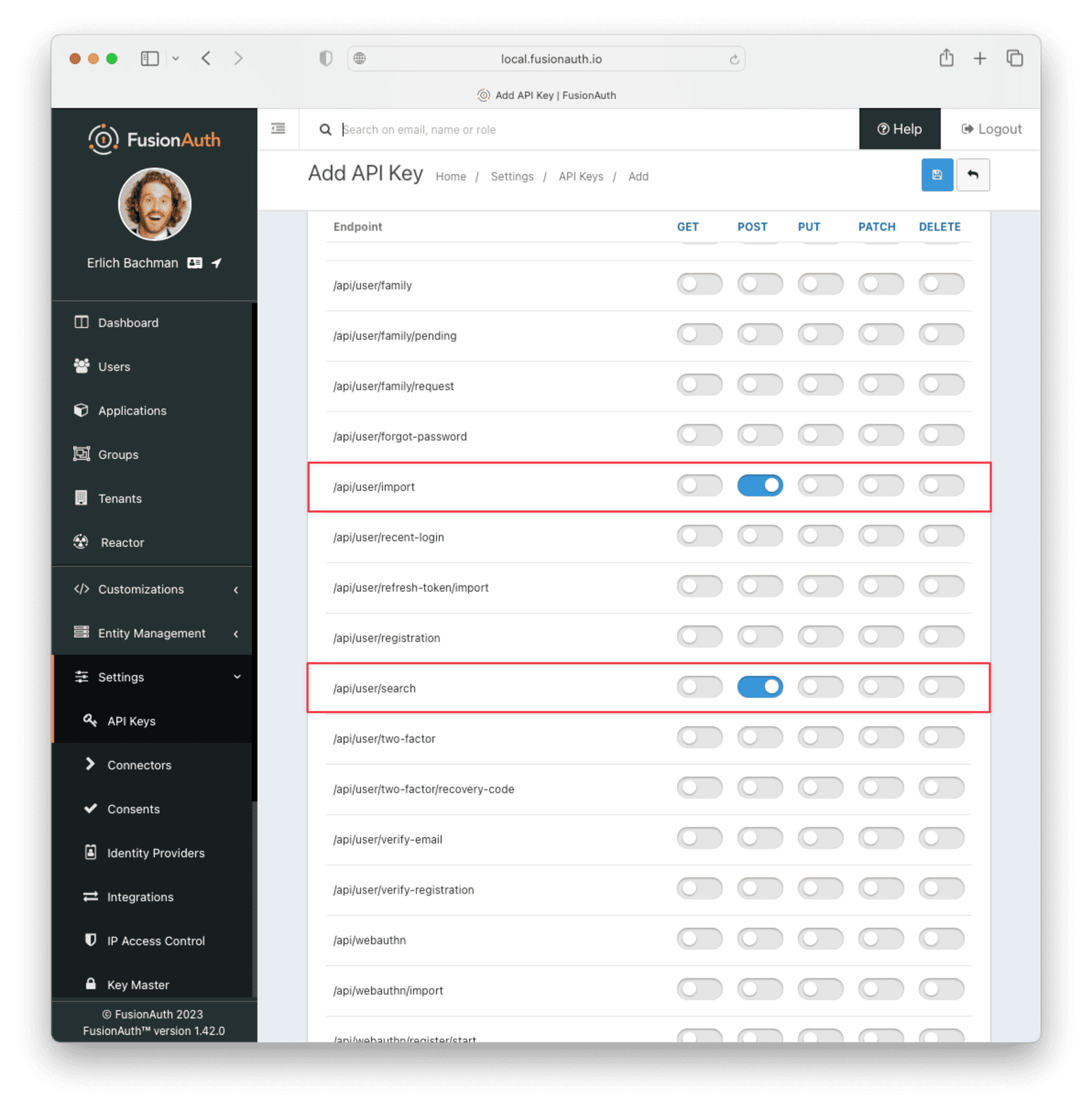
This key needs to have the permission to run a bulk import of users. In the spirit of the principle of least privilege, give it only the following permissions:
POSTto the/api/user/importendpoint.POSTto the/api/user/searchendpoint.POSTto the/api/identity-provider/linkendpoint (not shown below).
Record the API key string, as you’ll use it below.
Get the Script
FusionAuth provides an import script under a permissive open-source license. It requires Ruby (tested with Ruby 2.7). To get the script, clone the Git repository:
Getting the import scripts
git clone https://github.com/FusionAuth/fusionauth-import-scriptsNavigate to the supabase directory:
cd fusionauth-import-scripts/supabaseInstall Needed Gems
The following gems must be available to the import script:
datejsonoptparsesecurerandomfusionauth_client
Most likely all of these will be on your system already, except the fusionauth_client gem.
If you have bundler installed, run bundle install in the supabase directory. Otherwise, install the needed gems in some other way.
Use the Script
You can see the output of the script by running it with the -h option:
Running the import script with the help command line switch
ruby ./import.rb -hThe output will be similar to this:
The help output of the import.rb script
Usage: import.rb [options]
-l, --link-social-accounts Link social accounts, if present, after import. This operation is slower than an import.
-r APPLICATION_IDS, A comma separated list of existing applications Ids. All users will be registered for these applications.
--register-users
-o, --only-link-social-accounts Link social accounts with no import.
-u, --users-file USERS_FILE The exported JSON user data file from Supabase. Defaults to users.json.
-f FUSIONAUTH_URL, The location of the FusionAuth instance. Defaults to http://localhost:9011.
--fusionauth-url
-k, --fusionauth-api-key API_KEY The FusionAuth API key.
-t TENANT_ID, The FusionAuth tenant id. Required if more than one tenant exists.
--fusionauth-tenant-id
-m, --map-supa-id Whether to map the Supabase id for normal imported users to the FusionAuth user id.
-h, --help Prints this help.For this script to work correctly, set the following switches, unless the defaults work for you:
-ushould point to the location of the user export file you obtained, unless the default works.-fmust point to your FusionAuth instance. If you are testing locally, it will probably behttp://localhost:9011.-kneeds to be set to the value of the API key created above.-tshould be set to the Id of the testing tenant created above.
The -o and -l switches will attempt to create links for any social users (where the user authenticated via Google or another social provider) found in the users data file.
If you are loading social users, you must create the social providers in FusionAuth beforehand, or the links will fail. Additionally, creating a link is not currently optimized in the same way that loading users is. So it may make sense to import all the users in one pass (omitting the -l switch). Then, after the users are imported, create the links using the -o switch in a second pass.
The social account linking functionality will only work with FusionAuth versions above or equal to 1.28. The fusionauth_client library must be >= 1.28 as well.
When you run the script:
Import script output
ruby ./import.rb -f http://localhost:9011 -k '...' -u users.json -t '...' -lYou’ll see output like:
Import script output
FusionAuth Importer : Supabase
> User file: users.json
> Call FusionAuth to import users
> Import success
Linking 2 social accounts
> Link success
> Link success
Duplicate users 0
Import complete. 4 users imported.Enhancing the Script
You may also want to migrate additional data. Currently, the following attributes are migrated:
user_idemailemail_verifiedusername- the password hash and supporting attributes, if available
If you have additional user attributes to migrate, review and modify the map_user method.
You may also want to assign Roles, or associate users with Groups, by creating the appropriate JSON data structures in the import call. These are documented in the
Import User API docs. This will require modifying the import.rb code.
Verify the Import
Next, log in to the FusionAuth administrative user interface. Review the user entries to ensure the data was correctly imported.
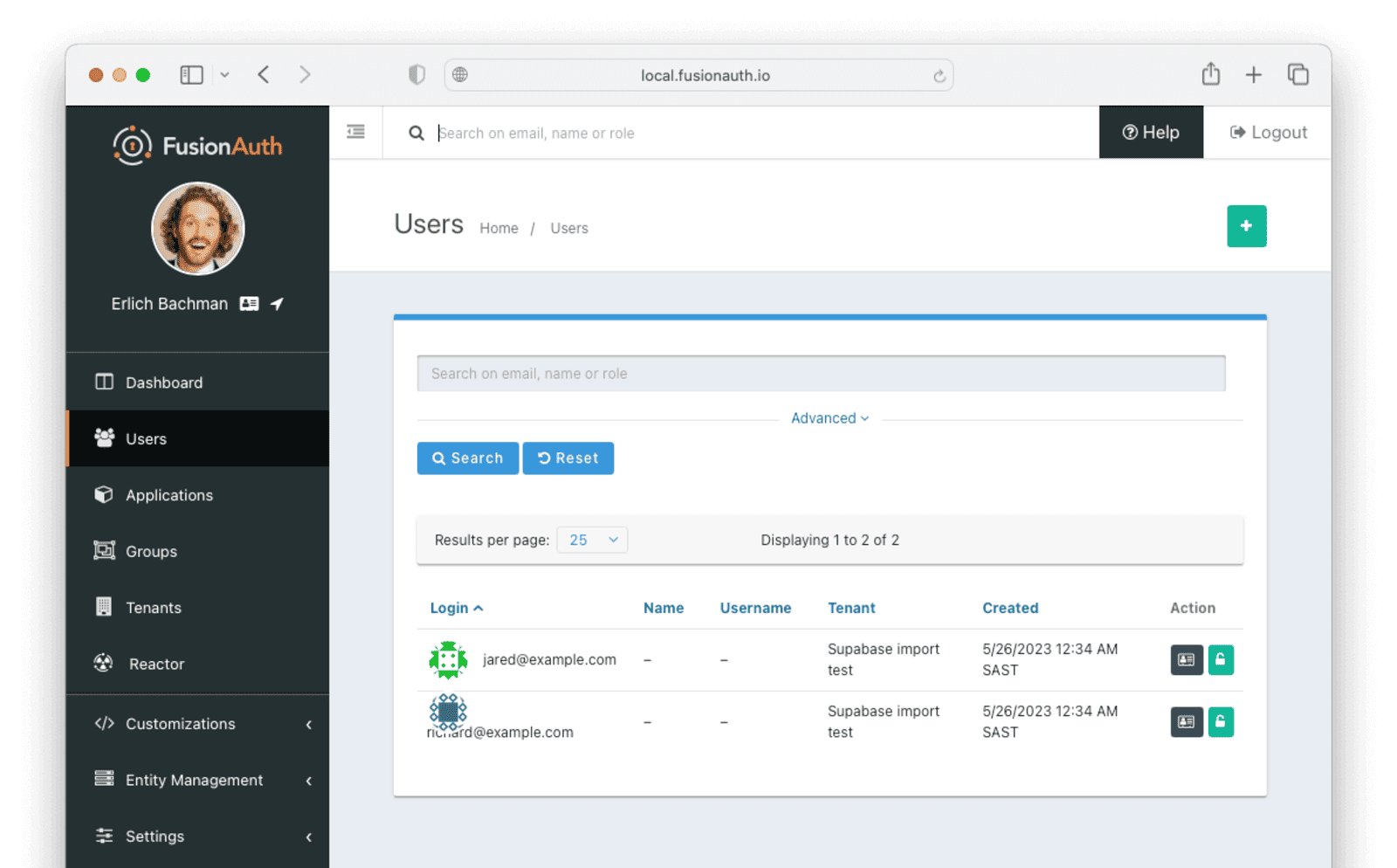
You can manage the user by clicking on the Manage button (black button) to the right of the Created date in the list to review the details of the imported user’s profile.
If you have a test user whose password you know, open an incognito window and log in to ensure the hash migration was successful. You recorded the URL to log in to the example application in Create a Test Application.
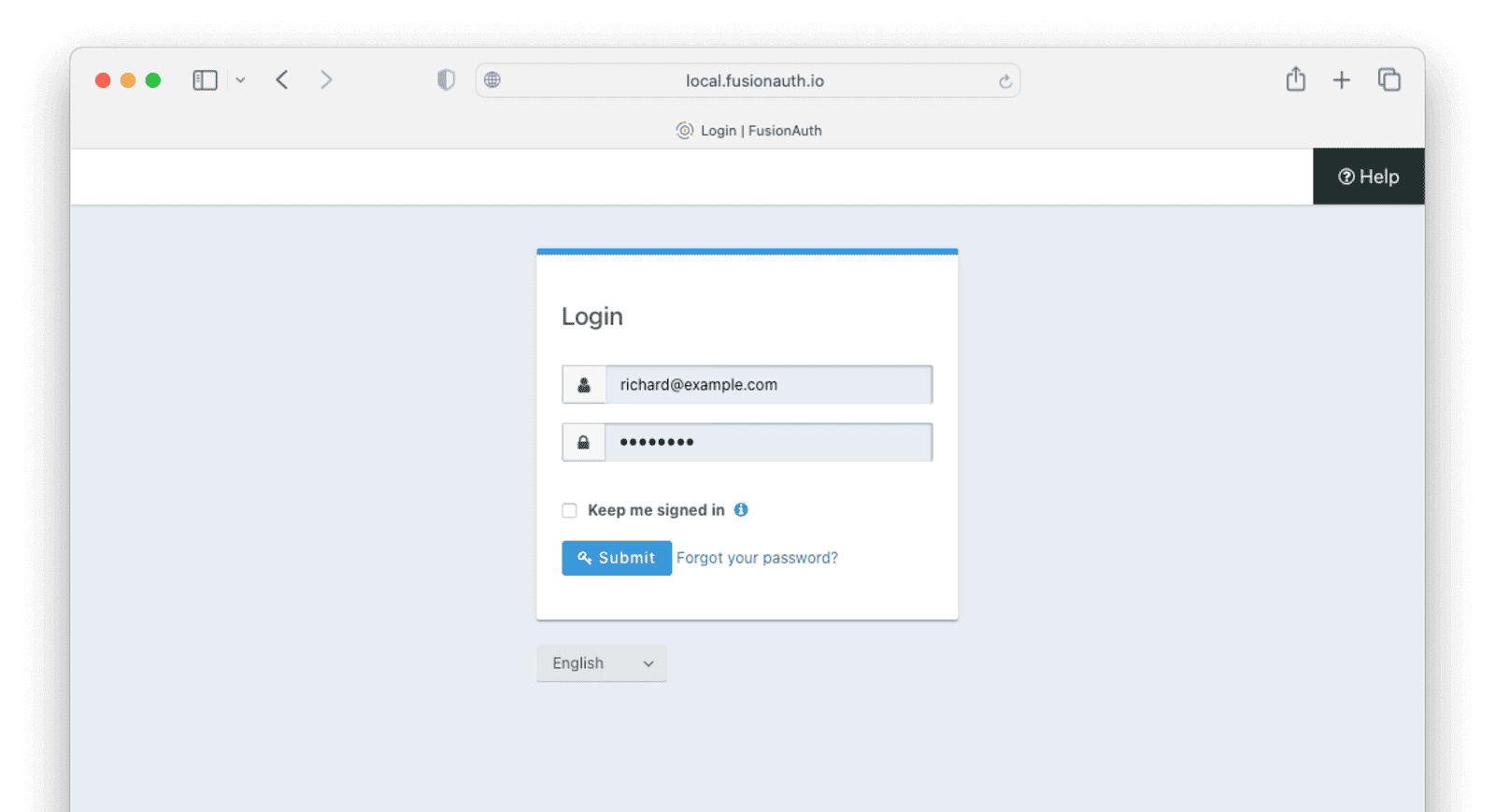
After the test login, the user will be redirected to a URL like https://example.com/?code=FlZF97WIYLNxt4SGD_22qvpRh4fZ6kg_N89ZbBAy1E4&locale=fr&userState=Authenticated. This happens because you haven't set up a web application to handle the authorization code redirect.
That is an important next step but is beyond the scope of this document. Consult the 5 minute setup guide for an example of how to do this.
The Final Destination of Imported Users
After you are done testing, you can choose to import users into the default tenant or a new tenant. Whichever you choose, make sure to update the -t switch to the correct value before running the import for the final time.
If you aren’t keeping users in the test tenant, delete it.
If you need to start over because the import failed or you need to tweak a setting, delete the tenant you created. This will remove all the users and other configurations for this tenant, giving you a fresh start. To do so, navigate to Tenants and choose the Delete button (trash can icon).
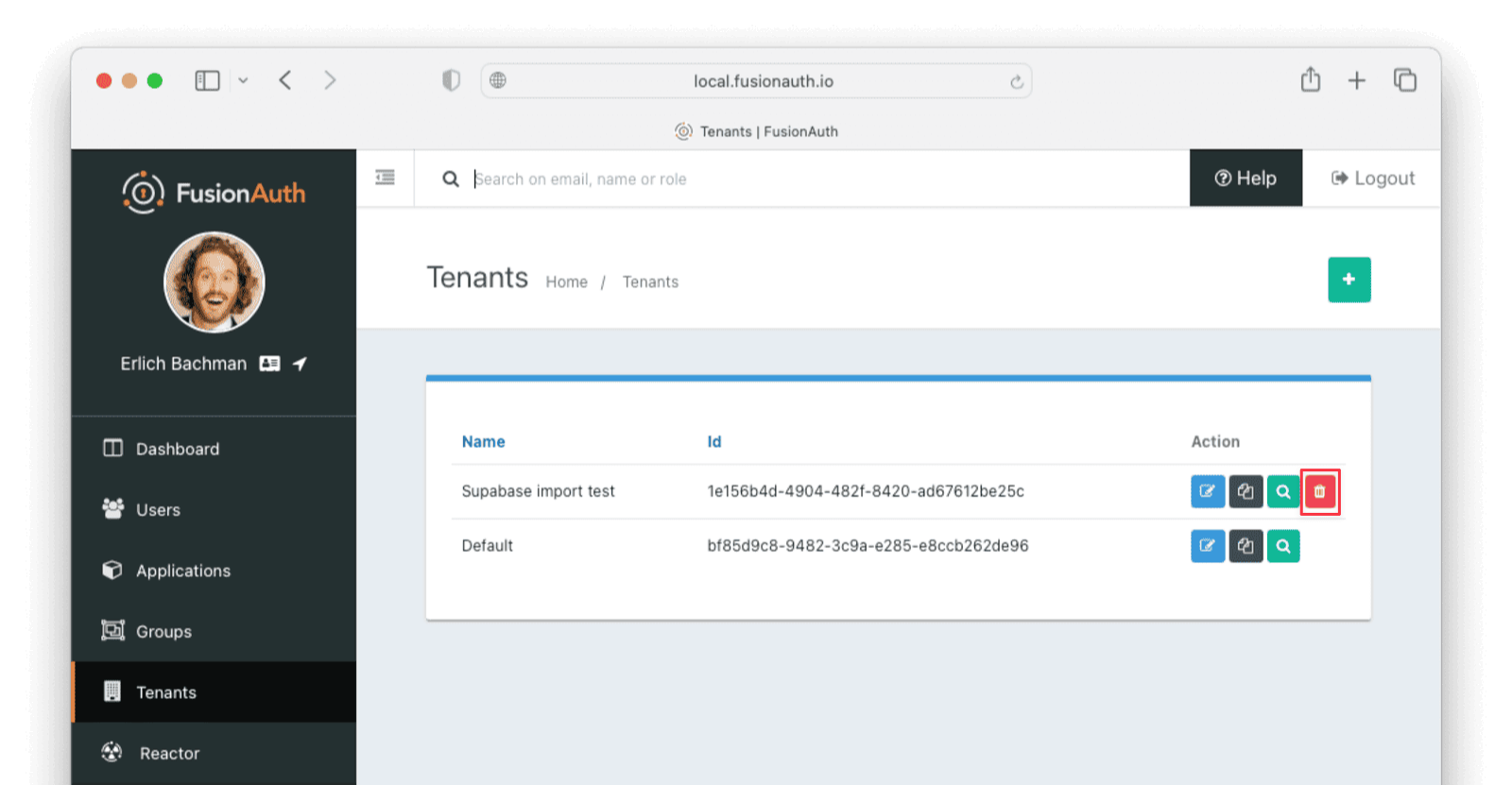
Confirm your desire to delete the tenant. Depending on how many users you have imported, this may take some time.
What to Do Next
You now have your users migrated, or a plan to do so. Congratulations! What is next?
You need to migrate additional configurations, as mentioned in Other Entities. Since the type of configuration varies, it is hard to provide a full list of how to import these items, but the general pattern will be:
- Identify corresponding FusionAuth functionality.
- Configure it in your FusionAuth instance, either manually or by scripting it using the client libraries or API.
- Update your application configuration to use the new FusionAuth functionality.
Make sure you assign your users to the appropriate FusionAuth applications. You can do this either:
- As part of your import process by adding registrations at import time.
- After users have been migrated with the Registrations API.
You’ll also need to modify and test each of your applications, whether custom, open source, or commercial, to ensure:
- Users can successfully log in.
- The authorization code redirect is handled correctly.
- Users receive appropriate permissions and roles based on the JWT.
- The look and feel of the hosted login pages matches each application’s look and feel.
If your application uses a standard OAuth, SAML or OIDC library to communicate with , the transition should be relatively painless.
Additional Support
If you need support in your migration beyond that provided in this guide, you may:
- Post in our forums and get support from the community.
- Purchase a support plan and get expert help from the Engineering Team.

